Cladistic association analysis of Y chromosome effects on alcohol dependence and related personality traits
- PMID: 10097188
- PMCID: PMC22445
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.7.4204
Cladistic association analysis of Y chromosome effects on alcohol dependence and related personality traits
Abstract
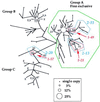
Association between Y chromosome haplotype variation and alcohol dependence and related personality traits was investigated in a large sample of psychiatrically diagnosed Finnish males. Haplotypes were constructed for 359 individuals using alleles at eight loci (seven microsatellite loci and a nucleotide substitution in the DYZ3 alphoid satellite locus). A cladogram linking the 102 observed haplotype configurations was constructed by using parsimony with a single-step mutation model. Then, a series of contingency tables nested according to the cladogram hierarchy were used to test for association between Y haplotype and alcohol dependence. Finally, using only alcohol-dependent subjects, we tested for association between Y haplotype and personality variables postulated to define subtypes of alcoholism-antisocial personality disorder, novelty seeking, harm avoidance, and reward dependence. Significant association with alcohol dependence was observed at three Y haplotype clades, with significance levels of P = 0.002, P = 0.020, and P = 0.010. Within alcohol-dependent subjects, no relationship was revealed between Y haplotype and antisocial personality disorder, novelty seeking, harm avoidance, or reward dependence. These results demonstrate, by using a fully objective association design, that differences among Y chromosomes contribute to variation in vulnerability to alcohol dependence. However, they do not demonstrate an association between Y haplotype and the personality variables thought to underlie the subtypes of alcoholism.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Personality traits and dopamine receptors (D2 and D4): linkage studies in families of alcoholics.Am J Med Genet. 1999 Dec 15;88(6):634-41. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1096-8628(19991215)88:6<634::aid-ajmg11>3.0.co;2-m. Am J Med Genet. 1999. PMID: 10581482
-
Evidence for linkage and association to alcohol dependence on chromosome 19.Genet Epidemiol. 1999;17 Suppl 1:S367-72. doi: 10.1002/gepi.1370170762. Genet Epidemiol. 1999. PMID: 10597464
-
Genetic heterogeneity and the classification of alcoholism.Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse. 1988;7(3-4):3-16. doi: 10.1300/J251v07n03_02. Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse. 1988. PMID: 3066194 Review.
-
WHO/ISBRA Study on State and Trait Markers of Alcohol Use and Dependence: analysis of demographic, behavioral, physiologic, and drinking variables that contribute to dependence and seeking treatment. International Society on Biomedical Research on Alcoholism.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002 Jul;26(7):1047-61. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2002. PMID: 12170115
-
Personality as an intermediate phenotype for genetic dissection of alcohol use disorder.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Jan;125(1):107-130. doi: 10.1007/s00702-016-1672-9. Epub 2017 Jan 4. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 28054193 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The diverse applications of cladistic analysis of molecular evolution, with special reference to nested clade analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Jan 8;11(1):124-39. doi: 10.3390/ijms11010124. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20162005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the use of haplotype phylogeny to detect disease susceptibility loci.BMC Genet. 2005 May 18;6:24. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-6-24. BMC Genet. 2005. PMID: 15904492 Free PMC article.
-
Y chromosome haplogroups in autistic subjects.Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7(2):217-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000968. Mol Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 11840316 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and epigenetic factors underlying sex differences in the regulation of gene expression in the brain.J Neurosci Res. 2017 Jan 2;95(1-2):301-310. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23886. J Neurosci Res. 2017. PMID: 27870402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of the Y Chromosome in Brain Function.Open Neuroendocrinol J. 2009;2:20-30. doi: 10.2174/1876528900902010020. Open Neuroendocrinol J. 2009. PMID: 20396406 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cloninger C R. Science. 1987;236:410–416. - PubMed
-
- Cloninger C R, Bohman M, Sigvardsson S. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981;38:861–868. - PubMed
-
- Cloninger C R. Nat Med. 1995;1:623–625. - PubMed
-
- Bohman M, Sigvardsson S, Cloninger C R. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1981;38:965–969. - PubMed
-
- Cadoret R J, Troughton E, O’Gorman T W, Heywood E. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1986;43:1131–1136. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

