Modes of action of acarbose hydrolysis and transglycosylation catalyzed by a thermostable maltogenic amylase, the gene for which was cloned from a Thermus strain
- PMID: 10103262
- PMCID: PMC91232
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.4.1644-1651.1999
Modes of action of acarbose hydrolysis and transglycosylation catalyzed by a thermostable maltogenic amylase, the gene for which was cloned from a Thermus strain
Abstract
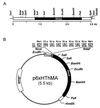
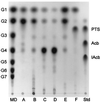
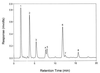
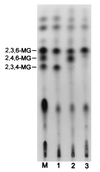
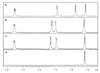
A maltogenic amylase gene was cloned in Escherichia coli from a gram-negative thermophilic bacterium, Thermus strain IM6501. The gene encoded an enzyme (ThMA) with a molecular mass of 68 kDa which was expressed by the expression vector p6xHis119. The optimal temperature of ThMA was 60 degrees C, which was higher than those of other maltogenic amylases reported so far. Thermal inactivation kinetic analysis of ThMA indicated that it was stabilized in the presence of 10 mM EDTA. ThMA harbored both hydrolysis and transglycosylation activities. It hydrolyzed beta-cyclodextrin and starch mainly to maltose and pullulan to panose. ThMA not only hydrolyzed acarbose, an amylase inhibitor, to glucose and pseudotrisaccharide (PTS) but also transferred PTS to 17 sugar acceptors, including glucose, fructose, maltose, cellobiose, etc. Structural analysis of acarbose transfer products by using methylation, thin-layer chromatography, high-performance ion chromatography, and nuclear magnetic resonance indicated that PTS was transferred primarily to the C-6 of the acceptors and at lower degrees to the C-3 and/or C-4. The transglycosylation of sugar to methyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside by forming an alpha-(1,3)-glycosidic linkage was demonstrated for the first time by using acarbose and ThMA. Kinetic analysis of the acarbose transfer products showed that the C-4 transfer product formed most rapidly but readily hydrolyzed, while the C-6 transfer product was stable and accumulated in the reaction mixture as the main product.
Figures



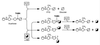
References
-
- Aleshin A E, Firsov L M, Honzatke R B. Refined structure for the complex of acarbose with glucoamylase from Aspergillus awamori var. X100 to 2.4-Å resolution. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:15631–15639. - PubMed
-
- BMDP statistical software. 1981. California State University.
-
- Bradford M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski A M, Davies M J. Structure of the Aspergillus oryzae α-amylase complexed with the inhibitor acarbose at 2.0 Å. Biochemistry. 1997;36:10837–10845. - PubMed
-
- Cha H J, Yoon H G, Kim Y W, Lee H S, Kim J W, Kweon K S, Oh B H, Park K H. Molecular and enzymatic characterization of novel maltogenic amylase that hydrolyzes and transglycosylates acarbose. Eur J Biochem. 1998;253:251–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

