Business, households, and government: health care spending, 1995
- PMID: 10170349
- PMCID: PMC4194499
Business, households, and government: health care spending, 1995
Abstract
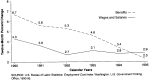
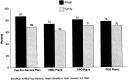
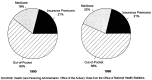
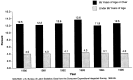
For the period 1990-95, we will present data on health care spending by business, households, and government. In addition, we will measure the relative impact of these expenditures on each sector's ability to pay. In 1994 and 1995, health care costs experienced the slowest growth in 3 decades. Combined with healthy revenue growth, slow cost growth helped ease or stabilize the financing burden faced by business, households and government.
Figures

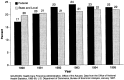

References
-
- Board of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. 1996 Annual Report of the Board of Trustees of the Federal Hospital Insurance Trust Fund. Washington DC: Jun 5, 1996.
-
- Board of Trustees of the Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund. 1996 Annual Report of the Board of Trustees of the Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund. Washington DC: Jun 5, 1995.
-
- KPMG Peat Marwick. Health Benefits in 1995. Newark, NJ.: 1995.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
