Suppression of nitric oxide synthase and the down-regulation of the activation of NFkappaB in macrophages by resveratrol
- PMID: 10188978
- PMCID: PMC1565862
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702357
Suppression of nitric oxide synthase and the down-regulation of the activation of NFkappaB in macrophages by resveratrol
Abstract
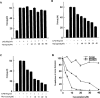
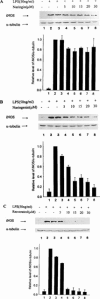
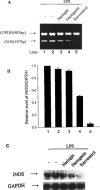
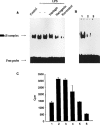
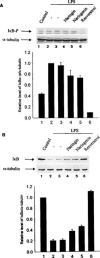
Resveratrol, naringenin and naringin are naturally occurring flavonoids in grapes and grapefruits. The anti-inflammatory effects of these flavonoids have been well documented, but the mechanism is poorly characterized. High concentration of NO are produced by inducible NO synthase (iNOS) in inflammation, and the prevention of the expression of iNOS may be an important anti-inflammatory mechanism. In this study, the effects of these flavonoids on the induction of NO synthase (NOS) in RAW 264.7 cells activated with bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS, 50 ng ml(-1)) were investigated. Resveratrol was found strongly to inhibit NO generation in activated macrophages, as measured by the amount of nitrite released into the culture medium, and resveratrol strongly reduced the amount of cytosolic iNOS protein and steady state mRNA levels. However, the inhibitory abilities of naringenin were lower, and the inhibitory abilities of naringin were almost negligible. In electrophoretic mobility shift assays, the activation of NFkappaB induced by LPS for 1 h was inhibited by resveratrol (30 microM). Furthermore, in immunoblotting analysis, cells treated with LPS plus resveratrol showed an inhibition of phosphorylation as well as degradation of IkappaBalpha, and a reduced nuclear content of NFkappaB subunits. The flavonoids may be of value for inhibiting the enhanced expression of iNOS in inflammation through down-regulation of NFkappaB binding activity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate blocks the induction of nitric oxide synthase by down-regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced activity of transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB.Mol Pharmacol. 1997 Sep;52(3):465-72. Mol Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9281609
-
Comparative studies on the suppression of nitric oxide synthase by curcumin and its hydrogenated metabolites through down-regulation of IkappaB kinase and NFkappaB activation in macrophages.Biochem Pharmacol. 2000 Dec 1;60(11):1665-76. doi: 10.1016/s0006-2952(00)00489-5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2000. PMID: 11077049
-
Suppressive effect of novel aromatic diamine compound on nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Oct 3;521(1-3):1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.07.013. Epub 2005 Sep 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16183054
-
Chemoprevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease by resveratrol.Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1999 Jul;23(3):99-106. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1999. PMID: 10492890 Review.
-
Role of PKC and tyrosine kinase in ethanol-mediated inhibition of LPS-inducible nitric oxide synthase.Alcohol. 1998 Aug;16(2):167-75. doi: 10.1016/s0741-8329(97)00187-0. Alcohol. 1998. PMID: 9665319 Review.
Cited by
-
Naringin Protects against Rotenone-induced Apoptosis in Human Neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y Cells.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009 Aug;13(4):281-5. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2009.13.4.281. Epub 2009 Aug 31. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19885011 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory properties of various natural chemopreventive agents on the activation of NF-kappaB signaling pathway.Pharm Res. 2004 Apr;21(4):661-70. doi: 10.1023/b:pham.0000022413.43212.cf. Pharm Res. 2004. PMID: 15139523
-
Resveratrol derivatives as promising chemopreventive agents with improved potency and selectivity.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011 Aug;55(8):1249-65. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201100122. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2011. PMID: 21714126 Free PMC article.
-
Novel resveratrol analogues attenuate renal ischemic injury in rats.J Surg Res. 2015 Feb;193(2):807-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2014.08.015. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Surg Res. 2015. PMID: 25214260 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory action of pterostilbene is mediated through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in colon cancer cells.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009 Jul;2(7):650-7. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-08-0224. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2009. PMID: 19549798 Free PMC article.
References
-
- BAEUERLE P.A., BALTIMORE D. NFκB: ten years after. Cell. 1996;87:13–20. - PubMed
-
- BALDWIN A.S., JR The NFκB and IκB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996;14:649–681. - PubMed
-
- BASTIAN N.R., HIBBS J.B., JR Assembly and regulation of NADPH oxidase and nitric oxide synthase. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 1994;6:131–139. - PubMed
-
- BRANDI M.I. Flavonoids: biochemical effects and therapeutic applications. Bone Miner. 1992;19:S3–S14. - PubMed
-
- CALOMME M., PIETERS L., VLIETINCK A., BERGHE D.M. Inhibition of bacterial mutagenesis by citrus flavonoids. Planta Medica. 1996;62:222–226. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

