Signalling by CXC-chemokine receptors 1 and 2 expressed in CHO cells: a comparison of calcium mobilization, inhibition of adenylyl cyclase and stimulation of GTPgammaS binding induced by IL-8 and GROalpha
- PMID: 10188995
- PMCID: PMC1565838
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702329
Signalling by CXC-chemokine receptors 1 and 2 expressed in CHO cells: a comparison of calcium mobilization, inhibition of adenylyl cyclase and stimulation of GTPgammaS binding induced by IL-8 and GROalpha
Abstract
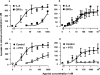
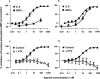
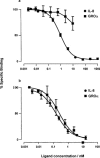
The effect of interleukin-8 (IL-8) and growth-related oncogene alpha (GROalpha) on [35S]-guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) ([35S]GTPgammaS) binding, forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation and cytosolic calcium concentration were determined in recombinant CHO cells expressing HA-tagged CXC-chemokine receptors 1 and 2 (CXCR1 and CXCR2). Radioligand binding assays confirmed that the binding profiles of the recombinant receptors were similar to those of the native proteins. IL-8 displaced [125I]-IL-8 binding to CXCR1 and CXCR2 with pKi values of 8.89+/-0.05 and 9.27+/-0.03, respectively. GROalpha, a selective CXCR2 ligand, had a pKi value of 9.66+/-0.39 at CXCR2 but a pKi>8 at CXCR1. Calcium mobilization experiments were also consistent with previous reports on native receptors. Activation of both receptors resulted in stimulation of [35S]GTPgammaS binding and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase. A comparison of the functional data at CXCRI showed that a similar potency order (IL-8> >GROalpha) was obtained in all three assays. However, at CXCR2 whilst the potency orders for calcium mobilization and inhibition of adenylyl cyclase were similar (IL-8 > or = GROalpha), the order was reversed for stimulation of [35S]GTPgammaS binding (GROalpha > IL-8). All of the functional responses at both receptors were inhibited by pertussis toxin (PTX), suggesting coupling to a Gi/Go protein. However, the calcium mobilization induced by IL-8 at CXCR1 was not fully inhibited by PTX, suggesting an interaction with a G-protein of the Gq family. Our results with pertussis toxin also suggested that, in the [35S]GTPgammaS binding assay, CXCR1 displays some constitutive activity. Thus, we have characterized the binding and several functional responses at HA-tagged CXCRs 1 and 2 and have shown that their pharmacology agrees well with that of the native receptors. We also have preliminary evidence that CXCR1 displays constitutive activity in our cell line and that CXCR2 may traffic between different PTX sensitive G-proteins.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CXCR2 stimulation primes CXCR1 [Ca2+]i responses to IL-8 in human neutrophils.Shock. 1999 Dec;12(6):428-37. doi: 10.1097/00024382-199912000-00003. Shock. 1999. PMID: 10588510
-
Mast cell migratory response to interleukin-8 is mediated through interaction with chemokine receptor CXCR2/Interleukin-8RB.Blood. 1999 May 1;93(9):2791-7. Blood. 1999. PMID: 10216072
-
Chemokine antagonists that discriminate between interleukin-8 receptors. Selective blockers of CXCR2.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jun 27;272(26):16166-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.26.16166. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9195914
-
Combined anti CXC receptors 1 and 2 therapy is a promising anti-inflammatory treatment for respiratory diseases by reducing neutrophil migration and activation.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015 Oct;34:37-45. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2015.08.002. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2015. PMID: 26271598 Review.
-
A role for CXCR2 in senescence, but what about in cancer?Cancer Res. 2009 Mar 15;69(6):2167-70. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3772. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19276354 Review.
Cited by
-
Alpha-defensin 1 (human neutrophil protein 1) as an antichemotactic agent for human polymorphonuclear leukocytes.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003 Aug;47(8):2666-8. doi: 10.1128/AAC.47.8.2666-2668.2003. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2003. PMID: 12878538 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple active states and oligomerization of CCR5 revealed by functional properties of monoclonal antibodies.Mol Biol Cell. 2002 Feb;13(2):723-37. doi: 10.1091/mbc.01-03-0129. Mol Biol Cell. 2002. PMID: 11854425 Free PMC article.
-
The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2013/14: G protein-coupled receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Dec;170(8):1459-581. doi: 10.1111/bph.12445. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24517644 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Human Cytomegalovirus Viral Chemokines, vCXCL-1s, Display Functional Selectivity for Neutrophil Signaling and Function.J Immunol. 2015 Jul 1;195(1):227-36. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400291. Epub 2015 May 18. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25987741 Free PMC article.
-
The chemokine CXCL1/growth related oncogene increases sodium currents and neuronal excitability in small diameter sensory neurons.Mol Pain. 2008 Sep 24;4:38. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-4-38. Mol Pain. 2008. PMID: 18816377 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AHUJA S.K., LEE J.C., MURPHY P.M. CXC chemokines bind to unique sets of selectivity determinants that can function independently and are broadly distributed on multiple domains of human interleukin-8 receptor B. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:225–232. - PubMed
-
- AHUJA S.K., MURPHY P.M. The CXC chemokines growth-related oncogene (GRO) α, GROβ, GROγ, neutrophil-activating peptide-2 and epithelial cell-derived neutrophil-activating peptide-78 are potent agonists for the type B, but not type A, human interleukin-8 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1996;271:20545–20550. - PubMed
-
- BACON K.B., CAMP R.D.R. Interleukin (IL)-8-induced in vitro human lymphocyte migration is inhibited by cholera and pertussis toxins and inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990;169:1099–1104. - PubMed
-
- BAGGIOLINI M., CLARK-LEWIS I. Interleukin-8, a chemo-tactic and inflammatory cytokine. FEBS Lett. 1992;307:97–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

