The subtype 2 of angiotensin II receptors and pressure-natriuresis in adult rat kidneys
- PMID: 10188997
- PMCID: PMC1565866
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702362
The subtype 2 of angiotensin II receptors and pressure-natriuresis in adult rat kidneys
Abstract
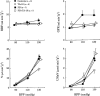
The present work examined the effects of the subtype 2 of angiotensin II (AT2) receptors on the pressure-natriuresis using a new peptide agonist, and the possible involvement of cyclic guanosine 3', 5' monophosphate (cyclic GMP) in these effects. In adult anaesthetized rats (Inactin, 100 mg kg(-1), i.p.) deprived of endogenous angiotensin II by angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition (quinapril, 10 mg kg(-1), i.v.), T2-(Ang II 4-8)2 (TA), a highly specific AT2 receptor agonist (5, 10 and 30 microg kg(-1) min(-1), i.v.) or its solvent was infused in four groups. Renal functions were studied at renal perfusion pressures (RPP) of 90, 110 and 130 mmHg and urinary cyclic GMP excretion when RPP was at 130 mmHg. The effects of TA (10 microg kg(-1) min(-1)) were reassessed in animals pretreated with PD 123319 (PD, 50 microg kg(-1) min(-1), i.v.), an AT2 receptor antagonist and the action of the same dose of PD alone was also determined. Increases in RPP from 90 to 130 mmHg did not change renal blood flow (RBF) but induced 8 and 15 fold increases in urinary flow and sodium excretion respectively. The 5 microg kg(-1) min(-1) dose of TA was devoid of action. The 10 and 30 microg kg(-1) min(-1) doses did not alter total RBF and glomerular filtration rate, but blunted pressure-diuresis and natriuresis relationships. These effects were abolished by PD. TA decreased urinary cyclic GMP excretion. After pretreatment with PD, this decrease was reversed to an increase which was also observed in animals receiving PD alone. In conclusion, renal AT2 receptors oppose the sodium and water excretion induced by acute increases in blood pressure and this action cannot be directly explained by changes in cyclic GMP.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effect of interactions between nitric oxide and angiotensin II on pressure diuresis and natriuresis.Am J Physiol. 1997 Nov;273(5):R1676-82. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1997.273.5.R1676. Am J Physiol. 1997. PMID: 9374809
-
Role of Mas receptor antagonist (A779) on pressure diuresis and natriuresis and renal blood flow in the absence of angiotensin II receptors type 1 and 2 in female and male rats.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Oct;65(5):633-9. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25371522
-
Renal angiotensin II AT2 receptors promote natriuresis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006 Feb;290(2):F503-8. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00092.2005. Epub 2005 Oct 4. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16204414
-
Renal mechanisms of angiotensin II-induced hypertension.Semin Nephrol. 2000 Sep;20(5):417-25. Semin Nephrol. 2000. PMID: 11022893 Review.
-
Dopamine and angiotensin as renal counterregulatory systems controlling sodium balance.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009 Jan;18(1):28-32. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32831a9e0b. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2009. PMID: 19077686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dominant factors that govern pressure natriuresis in diuresis and antidiuresis: a mathematical model.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014 May 1;306(9):F952-69. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00500.2013. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24553433 Free PMC article.
-
Renal autoregulation in health and disease.Physiol Rev. 2015 Apr;95(2):405-511. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00042.2012. Physiol Rev. 2015. PMID: 25834230 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal nutrient restriction in sheep: hypertension and decreased nephron number in offspring at 9 months of age.J Physiol. 2005 May 15;565(Pt 1):137-47. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.084202. Epub 2005 Mar 24. J Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15790663 Free PMC article.
-
Update: role of the angiotensin type-2 (AT(2)) receptor in blood pressure regulation.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2000 Apr;2(2):198-201. doi: 10.1007/s11906-000-0082-3. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2000. PMID: 10981149 Review.
-
Angiotensin AT2 receptors: cardiovascular hope or hype?Br J Pharmacol. 2003 Nov;140(5):809-24. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0705448. Epub 2003 Oct 6. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 14530223 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- ARIMA S., ITO S., OMATA K., TSUNODA K., YAOITA H., ABE K.Activation of angiotensin II type 2 receptor (AT2) causes epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs)-dependent vasodilation in the micro-perfused rabbit afferent arterioles Hypertension 199628515(abstract)
-
- CHANG R.S.L., LOTTI V.J. Angiotensin receptor subtypes in rat, rabbit, and monkey tissues: Relative distribution and species dependency. Life Sci. 1991;49:1485–1490. - PubMed
-
- CHATZIANTONIOU C., ARENDSHORST W.J. Angiotensin receptor sites in renal vasculature of rats developing genetic hypertension. Am. J. Physiol. 1993;265:F853–F862. - PubMed
-
- COGAN M.G., LIU F.Y., WONG P.C., TIMMERMANS P.B.M.W.M. Comparison of inhibitory potency by nonpeptide angiotensin II receptor antagonists PD 123177 and Dup 753 on proximal nephron and renal transport. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1991;259:687–691. - PubMed
-
- ENDO Y., ARIMA S., YAOITA H., OMATA K., TSUNODA K., TAKEUCHI K., ABE K., ITO S. Function of angiotensin II type 2 receptor in the postglomerular efferent arteriole. Kidney Int. 1997;52 Suppl. 63:S205–S207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

