TRANCE, a tumor necrosis factor family member critical for CD40 ligand-independent T helper cell activation
- PMID: 10190893
- PMCID: PMC2193017
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1025
TRANCE, a tumor necrosis factor family member critical for CD40 ligand-independent T helper cell activation
Abstract
CD40 ligand (CD40L), a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family member, plays a critical role in antigen-specific T cell responses in vivo. CD40L expressed on activated CD4(+) T cells stimulates antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, resulting in the upregulation of costimulatory molecules and the production of various inflammatory cytokines required for CD4(+) T cell priming in vivo. However, CD40L- or CD40-deficient mice challenged with viruses mount protective CD4(+) T cell responses that produce normal levels of interferon gamma, suggesting a CD40L/CD40-independent mechanism of CD4(+) T cell priming that to date has not been elucidated. Here we show that CD4(+) T cell responses to viral infection were greatly diminished in CD40-deficient mice by administration of a soluble form of TNF-related activation-induced cytokine receptor (TRANCE-R) to inhibit the function of another TNF family member, TRANCE. Thus, the TRANCE/TRANCE-R interaction provides costimulation required for efficient CD4(+) T cell priming during viral infection in the absence of CD40L/CD40. These results also indicate that not even the potent inflammatory microenvironment induced by viral infections is sufficient to elicit efficient CD4(+) T cell priming without proper costimulation provided by the TNF family (CD40L or TRANCE). Moreover, the data suggest that TRANCE/TRANCE-R may be a novel and important target for immune intervention.
Figures


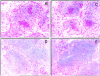

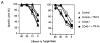
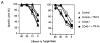
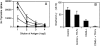

Comment in
-
TRANCE-RANK, a new signal pathway involved in lymphocyte development and T cell activation.J Exp Med. 1999 Apr 5;189(7):1017-20. doi: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1017. J Exp Med. 1999. PMID: 10190891 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Foy TM, Aruffo A, Bajorah J, Buhlmann JE, Noelle RJ. Immune regulation by CD40 and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1996;14:591–617. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Flavell RA. CD40 and CD154 in cell-mediated immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:111–136. - PubMed
-
- Van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40-CD40 ligand: a multifunctional receptor-ligand pair. Adv Immunol. 1996;61:1–77. - PubMed
-
- Grewal IS, Xu J, Flavell RA. Impairment of antigen-specific T-cell priming in mice lacking CD40 ligand. Nature. 1995;378:617–620. - PubMed
-
- van Essen D, Kikutani H, Gray D. CD40 ligand-transduced co-stimulation of T cells in the development of helper function. Nature. 1995;378:620–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

