Effector cells of both nonhemopoietic and hemopoietic origin are required for interferon (IFN)-gamma- and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-dependent host resistance to the intracellular pathogen, Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 10190899
- PMCID: PMC2192999
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.189.7.1083
Effector cells of both nonhemopoietic and hemopoietic origin are required for interferon (IFN)-gamma- and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha-dependent host resistance to the intracellular pathogen, Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
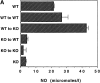
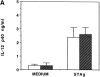
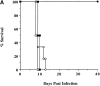
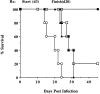
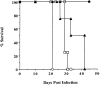
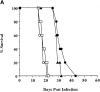
Although interferon (IFN)-gamma-activated, mononuclear phagocytes are considered to be the major effectors of resistance to intracellular pathogens, it is unclear how they control the growth of microorganisms that reside in nonhemopoietic cells. Pathogens within such cells may be killed by metabolites secreted by activated macrophages or, alternatively, directly controlled by cytokine-induced microbicidal mechanisms triggered within infected nonphagocytic cells. To distinguish between these two basic mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity, reciprocal bone marrow chimeras were constructed between wild-type and IFN-gamma receptor-deficient mice and their survival assessed following infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a protozoan parasite that invades both hemopoietic and nonhemopoietic cell lineages. Resistance to acute and persistent infection was displayed only by animals in which IFN-gamma receptors were expressed in both cellular compartments. Parallel chimera experiments performed with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-deficient mice also indicated a codependence on hemopoietic and nonhemopoietic lineages for optimal control of the parasite. In contrast, in mice chimeric for inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), an enzyme associated with IFN-gamma-induced macrophage microbicidal activity, expression by cells of hemopoietic origin was sufficient for host resistance. Together, these findings suggest that, in concert with bone marrow-derived effectors, nonhemopoietic cells can directly mediate, in the absence of endogenous iNOS, IFN-gamma- and TNF-alpha-dependent host resistance to intracellular infection.
Figures






References
-
- Biron CA, Gazzinelli RT. Effects of IL-12 on immune responses to microbial infection: a key mediator in regulating disease outcome. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995;7:485–496. - PubMed
-
- Unanue ER. Why listeriosis? A perspective on cellular immunity to infection. Immunol Rev. 1997;158:5–9. - PubMed
-
- Reiner SL, Locksley RM. The regulation of immunity to Leishmania major. . Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:151–177. - PubMed

