Effects of the prostanoid EP3-receptor agonists M&B 28767 and GR 63799X on infarct size caused by regional myocardial ischaemia in the anaesthetized rat
- PMID: 10193764
- PMCID: PMC1571228
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702348
Effects of the prostanoid EP3-receptor agonists M&B 28767 and GR 63799X on infarct size caused by regional myocardial ischaemia in the anaesthetized rat
Abstract
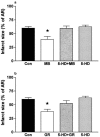
1. This study investigates the effects of two agonists of the prostanoid EP3-receptor (M&B 28767 and GR 63799X) on the infarct size caused by regional myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion in the anaesthetized rat. 2. One hundred and sixty-seven, male Wistar rats were anaesthetized (thiopentone, 120 mg kg(-1) i.p.), ventilated (8-10 ml kg(-1), 70 strokes min(-1), inspiratory oxygen concentration: 30%; PEEP: 1-2 mmHg) and subjected to occlusion of the left anterior descending coronary artery (LAD, for 7.5, 15, 25, 35, 45 or 60 min) followed by reperfusion (2 h). Infarct size was determined by staining of viable myocardium with a tetrazolium stain (NBT), histological evaluation by light and electron microscopy and determination of the plasma levels of cardiac troponin T. 3. M&B 28767 (0.5 microg kg(-1) min(-1), i.v., n=7) or GR 63799X (3 microg kg(-1) min(-1), i.v., n=7) caused significant reductions in infarct size from 60+/-3% (25 min ischaemia and 2 h reperfusion; saline-control, n=8) to 39+/-6 and 38+/-4% of the area at risk, without causing a significant fall in blood pressure. Pretreatment of rats with 5-hydroxydecanoate (5-HD), an inhibitor of ATP-sensitive potassium channels, attenuated the cardioprotective effects of both EP3-receptor agonists. The reduction in infarct size afforded by M&B 28767 was also abolished by glibenclamide and the protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitors staurosporine and chelerythrine. 4. Thus, M&B 28767 and GR 63799X reduce myocardial infarct size in the rat by a mechanism(s) which involves the activation of PKC and the opening of ATP-sensitive potassium channels.
Figures





References
-
- ADAMS J.E., ABENDSCHEIN D.R., JAFFE A.S. Biochemical markers of myocardial injury: is MB creatine kinase the choice for 1990s. Circ. 1993;88:750–763. - PubMed
-
- BALLER D., BRETSCHNEIDER H.J., HELLIGE G. A critical look at currently used indices of myocardial oxygen consumption. Basic Res. Cardiol. 1981;76:163–181. - PubMed
-
- BANCROFT J.D., STEVENS A. Theory and Practice of Histological Techniques 1995Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone; ed. Bancroft, J.D. & Stevens, A
-
- BAROLDI G. Different types of myocardial necrosis in coronary heart disease: A pathophysiological review of their functional significance. Am. Heart. J. 1975;89:742–752. - PubMed
-
- COLEMAN R.A., KENNEDY I., HUMPHREY P.P.A., BUNCE K., LUMLEY P. Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry 1990Oxford: Pergamon Press; 643ed. Hansch, C., Samnes, P.G., Taylor, J.B. & Emmett, J.C. p
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

