Protein-protein interaction in insulin signaling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance
- PMID: 10194465
- PMCID: PMC408269
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI6609
Protein-protein interaction in insulin signaling and the molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance
Figures
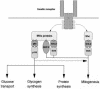
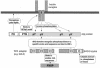

References
-
- White MF. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin action. Mol Cell Biochem. 1998;182:3–11. - PubMed
-
- Sudol M. From SRC homology domains to other signaling modules: proposal of the ‘protein recognition code’. Oncogene. 1998;17:1469–1474. - PubMed
-
- Yenush L, et al. The pleckstrin homology domain is the principle link between the insulin receptor and IRS-1. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:24300–24306. - PubMed
-
- Wolf G, et al. The PTB domains of IRS-1 and Shc have distinct but overlapping specificities. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:27407–27410. - PubMed
-
- Eck MJ, Dhe-Paganon S, Trub T, Nolte RT, Shoelson SE. Structure of the IRS-1 PTB domain bound to the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor. Cell. 1996;85:695–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

