Distinct affinity of binding sites for S-layer homologous domains in Clostridium thermocellum and Bacillus anthracis cell envelopes
- PMID: 10198008
- PMCID: PMC93670
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.181.8.2455-2458.1999
Distinct affinity of binding sites for S-layer homologous domains in Clostridium thermocellum and Bacillus anthracis cell envelopes
Abstract
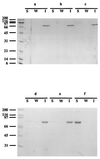
Binding parameters were determined for the SLH (S-layer homologous) domains from the Clostridium thermocellum outer layer protein OlpB, from the C. thermocellum S-layer protein SlpA, and from the Bacillus anthracis S-layer proteins EA1 and Sap, using cell walls from C. thermocellum and B. anthracis. Each SLH domain bound to C. thermocellum and B. anthracis cell walls with a different KD, ranging between 7.1 x 10(-7) and 1.8 x 10(-8) M. Cell wall binding sites for SLH domains displayed different binding specificities in C. thermocellum and B. anthracis. SLH-binding sites were not detected in cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. Cell walls of C. thermocellum lost their affinity for SLH domains after treatment with 48% hydrofluoric acid but not after treatment with formamide or dilute acid. A soluble component, extracted from C. thermocellum cells by sodium dodecyl sulfate treatment, bound the SLH domains from C. thermocellum but not those from B. anthracis proteins. A corresponding component was not found in B. anthracis.
Figures



References
-
- Gibson T J. Studies on the Epstein-Barr virus genome. Ph.D. thesis. Cambridge, England: University of Cambridge; 1984.
-
- Lemaire M, Miras I, Gounon P, Béguin P. Identification of a region responsible for binding to the cell wall within the S-layer protein of Clostridium thermocellum. Microbiology. 1998;144:211–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

