The membrane-attached electron carrier cytochrome cy from Rhodobacter sphaeroides is functional in respiratory but not in photosynthetic electron transfer
- PMID: 10200265
- PMCID: PMC16335
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4348
The membrane-attached electron carrier cytochrome cy from Rhodobacter sphaeroides is functional in respiratory but not in photosynthetic electron transfer
Abstract
Rhodobacter species are useful model organisms for studying the structure and function of c type cytochromes (Cyt c), which are ubiquitous electron carriers with essential functions in cellular energy and signal transduction. Among these species, Rhodobacter capsulatus has a periplasmic Cyt c2Rc and a membrane-bound bipartite Cyt cyRc. These electron carriers participate in both respiratory and photosynthetic electron-transfer chains. On the other hand, until recently, Rhodobacter sphaeroides was thought to have only one of these two cytochromes, the soluble Cyt c2Rs. Recent work indicated that this species has a gene, cycYRs, that is highly homologous to cycYRc, and in the work presented here, functional properties of its gene product (Cyt cyRs) are defined. It was found that Cyt cyRs is unable to participate in photosynthetic electron transfer, although it is active in respiratory electron transfer, unlike its R. capsulatus counterpart, Cyt cyRc. Chimeric constructs have shown that the photosynthetic incapability of Cyt cyRs is caused, at least in part, by its redox active subdomain, which carries the covalently bound heme. It, therefore, seems that this domain interacts differently with distinct redox partners, like the photochemical reaction center and the Cyt c oxidase, and allows the bacteria to funnel electrons efficiently to various destinations under different growth conditions. These findings raise an intriguing evolutionary issue in regard to cellular apoptosis: why do the mitochondria of higher organisms, unlike their bacterial ancestors, use only one soluble electron carrier in their respiratory electron-transport chains?
Figures

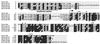

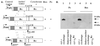
Similar articles
-
Mobile cytochrome c2 and membrane-anchored cytochrome cy are both efficient electron donors to the cbb3- and aa3-type cytochrome c oxidases during respiratory growth of Rhodobacter sphaeroides.J Bacteriol. 2001 Mar;183(6):2013-24. doi: 10.1128/JB.183.6.2013-2024.2001. J Bacteriol. 2001. PMID: 11222600 Free PMC article.
-
A novel membrane-associated c-type cytochrome, cyt cy, can mediate the photosynthetic growth of Rhodobacter capsulatus and Rhodobacter sphaeroides.EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1283-92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05773.x. EMBO J. 1993. PMID: 8385603 Free PMC article.
-
Cytochrome c(y) of Rhodobacter capsulatus is attached to the cytoplasmic membrane by an uncleaved signal sequence-like anchor.J Bacteriol. 1997 Apr;179(8):2623-31. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.8.2623-2631.1997. J Bacteriol. 1997. PMID: 9098061 Free PMC article.
-
The structure and function of the cytochrome c2: reaction center electron transfer complex from Rhodobacter sphaeroides.Photosynth Res. 2005;85(1):101-14. doi: 10.1007/s11120-005-1368-8. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 15977062 Review.
-
Structural and functional studies on the tetraheme cytochrome subunit and its electron donor proteins: the possible docking mechanisms during the electron transfer reaction.Photosynth Res. 2005;85(1):87-99. doi: 10.1007/s11120-004-2416-5. Photosynth Res. 2005. PMID: 15977061 Review.
Cited by
-
Stability of the cbb3-type cytochrome oxidase requires specific CcoQ-CcoP interactions.J Bacteriol. 2008 Aug;190(16):5576-86. doi: 10.1128/JB.00534-08. Epub 2008 Jun 13. J Bacteriol. 2008. PMID: 18556791 Free PMC article.
-
Photosynthesis research in Italy: a review.Photosynth Res. 2006 Jun;88(3):211-40. doi: 10.1007/s11120-006-9054-z. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Photosynth Res. 2006. PMID: 16755326 Review.
-
Uncovering the molecular mode of action of the antimalarial drug atovaquone using a bacterial system.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 22;280(29):27458-65. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502319200. Epub 2005 May 24. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15917236 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane-spanning and periplasmic segments of CcmI have distinct functions during cytochrome c Biogenesis in Rhodobacter capsulatus.J Bacteriol. 2007 Feb;189(3):789-800. doi: 10.1128/JB.01441-06. Epub 2006 Nov 22. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17122341 Free PMC article.
-
Tellurite and Selenite: how can these two oxyanions be chemically different yet so similar in the way they are transformed to their metal forms by bacteria?Biol Res. 2022 Apr 5;55(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s40659-022-00378-2. Biol Res. 2022. PMID: 35382884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

