Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with the 70-kDa S6 kinase and is activated by inhibition of FKBP12-rapamycinassociated protein
- PMID: 10200280
- PMCID: PMC16350
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4438
Protein phosphatase 2A interacts with the 70-kDa S6 kinase and is activated by inhibition of FKBP12-rapamycinassociated protein
Abstract
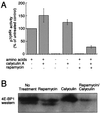
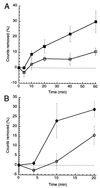
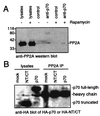
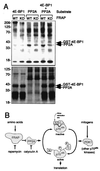
The FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein (FRAP; also called RAFT1/mTOR) regulates translation initiation and entry into the cell cycle. Depriving cells of amino acids or treating them with the small molecule rapamycin inhibits FRAP and results in rapid dephosphorylation and inactivation of the translational regulators 4E-BP1(eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1) and p70(s6k) (the 70-kDa S6 kinase). Data published recently have led to the view that FRAP acts as a traditional mitogen-activated kinase, directly phosphorylating 4E-BP1 and p70(s6k) in response to mitogenic stimuli. We present evidence that FRAP controls 4E-BP1 and p70(s6k) phosphorylation indirectly by restraining a phosphatase. A calyculin A-sensitive phosphatase is required for the rapamycin- or amino acid deprivation-induced dephosphorylation of p70(s6k), and treatment of Jurkat I cells with rapamycin increases the activity of the protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) toward 4E-BP1. PP2A is shown to associate with p70(s6k) but not with a mutated p70(s6k) that is resistant to rapamycin- and amino acid deprivation-mediated dephosphorylation. FRAP also is shown to phosphorylate PP2A in vitro, consistent with a model in which phosphorylation of PP2A by FRAP prevents the dephosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and p70(s6k), whereas amino acid deprivation or rapamycin treatment inhibits FRAP's ability to restrain the phosphatase.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998 Feb 17;95(4):1432-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.4.1432. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998. PMID: 9465032 Free PMC article.
-
Cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling of FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein is involved in rapamycin-sensitive signaling and translation initiation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Dec 19;97(26):14340-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.011511898. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 11114166 Free PMC article.
-
FKBP12-rapamycin-associated protein (FRAP) autophosphorylates at serine 2481 under translationally repressive conditions.J Biol Chem. 2000 Mar 10;275(10):7416-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.10.7416. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10702316
-
TOR action in mammalian cells and in Caenorhabditis elegans.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004;279:115-38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-18930-2_8. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2004. PMID: 14560955 Review.
-
p70 S6 kinase as a therapeutic target in cancers: More than just an mTOR effector.Cancer Lett. 2022 Jun 1;535:215593. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2022.215593. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Cancer Lett. 2022. PMID: 35176419 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein phosphatase 2A enables expression of interleukin 17 (IL-17) through chromatin remodeling.J Biol Chem. 2013 Sep 13;288(37):26775-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.483743. Epub 2013 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23918926 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of cap-dependent translation in mitosis.Genes Dev. 2001 Aug 15;15(16):2083-93. doi: 10.1101/gad.889201. Genes Dev. 2001. PMID: 11511540 Free PMC article.
-
The Arabidopsis homolog of yeast TAP42 and mammalian alpha4 binds to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatase 2A and is induced by chilling.Plant Physiol. 1999 Oct;121(2):609-17. doi: 10.1104/pp.121.2.609. Plant Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10517853 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus infection alters the eIF4F translation initiation complex and causes dephosphorylation of the eIF4E binding protein 4E-BP1.J Virol. 2002 Oct;76(20):10177-87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.76.20.10177-10187.2002. J Virol. 2002. PMID: 12239292 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Herbal Medicine as a Treatment Strategy for Myocardial Infarction through the Regulation of Angiogenesis.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 12;2022:8831750. doi: 10.1155/2022/8831750. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35600953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown E J, Schreiber S L. Cell. 1996;86:517–520. - PubMed
-
- Hara K, Yonezawa K, Weng Q-P, Kozlowski M T, Belham C, Avruch J. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:14484–14494. - PubMed
-
- Brown E J, Beal P A, Keith C T, Chen J, Shin T B, Schreiber S L. Nature (London) 1995;377:441–446. - PubMed
-
- Thomas G, Hall M N. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997;9:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Farmer J D, Jr, Lane W S, Friedman J, Weissman I, Schreiber S L. Cell. 1991;66:807–815. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

