Prevention of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by a polyphenolic fraction from green tea
- PMID: 10200295
- PMCID: PMC16365
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4524
Prevention of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by a polyphenolic fraction from green tea
Abstract
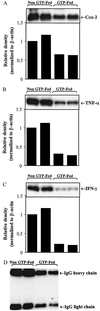
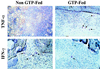
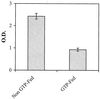
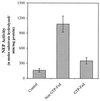
Identification of common dietary substances capable of affording protection or modulating the onset and severity of arthritis may have important human health implications. An antioxidant-rich polyphenolic fraction isolated from green tea (green tea polyphenols, GTPs) has been shown to possess anti-inflammatory and anticarcinogenic properties in experimental animals. In this study we determined the effect of oral consumption of GTP on collagen-induced arthritis in mice. In three independent experiments mice given GTP in water exhibited significantly reduced incidence of arthritis (33% to 50%) as compared with mice not given GTP in water (84% to 100%). The arthritis index also was significantly lower in GTP-fed animals. Western blot analysis showed a marked reduction in the expression of inflammatory mediators such as cyclooxygenase 2, IFN-gamma, and tumor necrosis factor alpha in arthritic joints of GTP-fed mice. Histologic and immunohistochemical analysis of the arthritic joints in GTP-fed mice demonstrated only marginal joint infiltration by IFN-gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha-producing cells as opposed to massive cellular infiltration and fully developed pannus in arthritic joints of non-GTP-fed mice. The neutral endopeptidase activity was approximately 7-fold higher in arthritic joints of non-GTP-fed mice in comparison to nonarthritic joints of unimmunized mice whereas it was only 2-fold higher in the arthritic joints of GTP-fed mice. Additionally, total IgG and type II collagen-specific IgG levels were lower in serum and arthritic joints of GTP-fed mice. Taken together our studies suggest that a polyphenolic fraction from green tea that is rich in antioxidants may be useful in the prevention of onset and severity of arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Haqqi T M, David C S. J Autoimmun. 1990;3:113–121. - PubMed
-
- Myers L K, Rosloniec E F, Cremer M A, Kang A H. Life Sci. 1997;61:1861–1878. - PubMed
-
- Haqqi T M, Qu X M, Sy M S, Banerjee S. Autoimmunity. 1995;20:163–170. - PubMed
-
- Durie F H, Fava R A, Noelle R J. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994;73:11–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

