Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma
- PMID: 10200299
- PMCID: PMC16369
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4546
Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma
Abstract
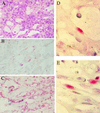
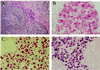
Human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8, also called KSHV) is linked to the etiopathogenesis of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS), multicentric Castleman's disease (MCD), and primary effusion lymphoma (PEL). The universal presence of HHV-8 in early KS has not yet been shown. We used a mAb (LN53) against latent nuclear antigen-1 (LNA-1) of HHV-8 encoded by ORF73 to study the distribution of the cell types latently infected by HHV-8 in patch, plaque, and nodular KS, MCD, and PEL. In early KS, HHV-8 is present in <10% of cells forming the walls of ectatic vessels. In nodular KS, HHV-8 is present in cells surrounding slit-like vessels and in >90% of spindle cells, but not in normal vascular endothelium. In addition, HHV-8 colocalizes with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3), a marker of lymphatic and precursor endothelium. In early KS lesions, VEGFR-3 is more extensively expressed than LNA-1, indicating that HHV-8 is not inducing the proliferation of VEGFR-3-positive endothelium directly. In MCD, HHV-8 is present in mantle zone large immunoblastic B cells. No staining for LNA-1 is seen in samples from multiple myeloma, prostate cancer, and angiosarcoma, supporting the absence of any etiological link between these diseases and HHV-8.
Figures




References
-
- Moore P S, Chang Y. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;147:217–221. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff C, Weiss R A. In: Advances in Cancer Research. Van de Woude G, Klein G, editors. Vol. 75. San Diego: Academic; 1998. pp. 57–86. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff C, Schulz T F, Kennedy M M, Graham A K, Fisher C, Thomas A, McGee J O, Weiss R A, O’Leary J J. Nat Med. 1995;1:1274–1278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

