Defective CD95/APO-1/Fas signal complex formation in the human autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, type Ia
- PMID: 10200300
- PMCID: PMC16370
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4552
Defective CD95/APO-1/Fas signal complex formation in the human autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, type Ia
Erratum in
- Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 May 18;101(20):7840
Abstract
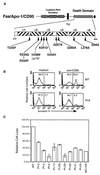
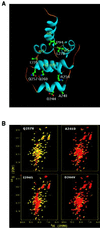
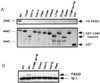
Heterozygous mutations in the CD95 (APO-1/Fas) receptor occur in most individuals with autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) and dominantly interfere with apoptosis by an unknown mechanism. We show that local or global alterations in the structure of the cytoplasmic death domain from nine independent ALPS CD95 death-domain mutations result in a failure to bind the FADD/MORT1 signaling protein. Despite heterozygosity for the abnormal allele, lymphocytes from ALPS patients showed markedly decreased FADD association and a loss of caspase recruitment and activation after CD95 crosslinking. These data suggest that intracytoplasmic CD95 mutations in ALPS impair apoptosis chiefly by disrupting death-domain interactions with the signaling protein FADD/MORT1.
Figures

References
-
- Hornung F, Chan F, Lenardo M J, McFarland H, Siegel R, Wang J, Zheng L. Annu Rev Immunol. 1999;17:221–253. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S, Golstein P. Science. 1995;267:1449–1456. - PubMed
-
- Tartaglia L A, Ayres T M, Wong G H, Goeddel D V. Cell. 1993;74:845–853. - PubMed
-
- Itoh N, Nagata S. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:10932–10937. - PubMed
-
- Boldin M P, Varfolomeev E E, Pancer Z, Mett I L, Camonis J H, Wallach D. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:7795–7798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

