A 500-bp region, approximately 40 kb upstream of the human CYP19 (aromatase) gene, mediates placenta-specific expression in transgenic mice
- PMID: 10200304
- PMCID: PMC16374
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.8.4575
A 500-bp region, approximately 40 kb upstream of the human CYP19 (aromatase) gene, mediates placenta-specific expression in transgenic mice
Abstract
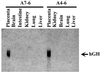
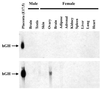
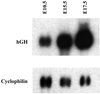
In humans, aromatase P450 (product of CYP19 gene), which catalyzes conversion of C19 steroids to estrogens, is expressed in a number of tissues, including ovary, adipose, and syncytiotrophoblast of the placenta. The 5' untranslated regions of CYP19 mRNA transcripts in these tissues are encoded by different tissue-specific first exons, which are spliced onto a common site just upstream of the translation initiation site in exon II. In placenta, the 5' untranslated region of CYP19 mRNA transcripts is encoded by exon I.1, which lies approximately 40 kb upstream of exon II. To map genomic sequences required for placenta-specific CYP19 expression, fusion genes containing 2,400 and 501 bp of placenta-specific exon I.1 5' flanking DNA linked to the human growth hormone gene (hGH), as reporter, were introduced into transgenic mice. Expression of CYP19(I.1):hGH fusion genes containing as little as 501 bp of 5' flanking DNA was placenta-specific and developmentally regulated. Furthermore, transgene expression occurred specifically in the labyrinthine trophoblast of the mouse placenta, which contains syncytial cells that may be analogous to the human syncytiotrophoblast. We show that a relatively small segment of DNA (approximately 500 bp) >40 kb upstream of the protein coding region of a human gene is able to direct expression in an appropriate tissue- and cell-specific manner in transgenic mice. These findings suggest that 5' flanking DNA within 501 bp of exon I.1 of the human CYP19 gene contains cis-acting elements that bind placenta-specific transcription factors that are conserved between humans and mice.
Figures
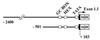
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the regulatory regions of the human aromatase (P450arom) gene involved in placenta-specific expression.Mol Endocrinol. 1998 Nov;12(11):1764-77. doi: 10.1210/mend.12.11.0190. Mol Endocrinol. 1998. PMID: 9817601
-
Genomic regions that mediate placental cell-specific and developmental regulation of human Cyp19 (aromatase) gene expression in transgenic mice.Endocrinology. 2005 May;146(5):2481-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1606. Epub 2005 Jan 27. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 15677755
-
A 278 bp region just upstream of the human CYP19 (aromatase) gene mediates ovary-specific expression in transgenic mice.Endocrinology. 2000 Jun;141(6):2050-3. doi: 10.1210/endo.141.6.7611. Endocrinology. 2000. PMID: 10830289
-
Mechanisms in the regulation of aromatase in developing ovary and placenta.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 Aug-Sep;106(1-5):62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.05.001. Epub 2007 May 21. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17596931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of transcriptional regulatory elements of the human aromatase cytochrome P450 gene (CYP19).J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):151-9. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00232-4. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603036 Review.
Cited by
-
CYP19A1 mediates severe SARS-CoV-2 disease outcome in males.Cell Rep Med. 2023 Sep 19;4(9):101152. doi: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101152. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Cell Rep Med. 2023. PMID: 37572667 Free PMC article.
-
Differential usage of alternate promoters of the human stress response gene ATF3 in stress response and cancer cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Apr;37(5):1438-51. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkn1082. Epub 2009 Jan 9. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19136462 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Genetic manipulation of the rodent placenta.Placenta. 2011 Mar;32 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S130-5. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2010.12.017. Epub 2011 Jan 22. Placenta. 2011. PMID: 21256588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroactive steroid exposure impacts neurodevelopment: Comparison of human and rodent placental contribution.J Neuroendocrinol. 2025 Jul;37(7):e13489. doi: 10.1111/jne.13489. Epub 2025 Jan 9. J Neuroendocrinol. 2025. PMID: 39789736 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) mediates stimulatory effects of estrogen on aromatase (CYP19) gene expression in human placenta.Mol Endocrinol. 2009 Jun;23(6):784-93. doi: 10.1210/me.2008-0371. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Mol Endocrinol. 2009. PMID: 19299445 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thompson E A, Jr, Siiteri P K. J Biol Chem. 1974;249:5373–5378. - PubMed
-
- Simpson E R, Mahendroo M S, Means G D, Kilgore M W, Hinshelwood M M, Graham-Lorence S, Amarneh B, Ito Y, Fisher C R, Michael M D, et al. Endocr Rev. 1994;15:342–355. - PubMed
-
- Fournet-Dulguerov N, MacLusky N J, Leranth C Z, Todd R G, Mendelson C R, Simpson E R, Naftolin F. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987;65:757–764. - PubMed
-
- Means G D, Mahendroo M S, Corbin J C, Mathis J M, Powell F E, Mendelson C R, Simpson E R. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:19385–19391. - PubMed
-
- Toda K, Terashima M, Kawamoto T, Sumimoto H, Yokoyama Y, Kuribayashi I, Mitsuuchi Y, Maeda T, Yamamoto Y, Sagara Y, et al. Eur J Biochem. 1990;193:559–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

