Studies of genetic relationships between bovine, caprine, cervine, and rangiferine alphaherpesviruses and improved molecular methods for virus detection and identification
- PMID: 10203465
- PMCID: PMC84742
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.5.1247-1253.1999
Studies of genetic relationships between bovine, caprine, cervine, and rangiferine alphaherpesviruses and improved molecular methods for virus detection and identification
Abstract
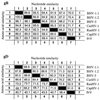
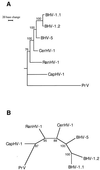
The glycoprotein B (gB) and D (gD) genes from five ruminant alphaherpesviruses, bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1), bovine herpesvirus 5 (BHV-5), caprine herpesvirus 1 (CapHV-1), cervine herpesvirus 1, and rangiferine herpesvirus 1, were partially sequenced. The nucleotide sequence alignments revealed a highly conserved gB gene, with homologies ranging between 87.2 and 99.6%, and a more variable gD gene, with homologies ranging between 71.3 and 98.9%. The phylogenetic analysis of the gB and gD nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences revealed that BHV-5 is the most closely related virus to the BHV-1 subtype 1 and BHV-1 subtype 2 cluster and that CapHV-1 is the most distantly related virus. The phylogenetic data showed a close relationship of all the studied viruses with suid herpesvirus 1. On the basis of sequence data for the gB gene, a nested PCR combined with restriction enzyme analysis (REA) of the PCR products was developed for the simultaneous detection and identification of the viruses that were studied. Nested primers from highly conserved sequence stretches were selected in order to amplify a region of 294 bp in all five viruses, and a subsequent REA of the PCR products allowed specific identification. A mimic molecule that served as an internal standard of the amplification efficiency was constructed. The practical diagnostic applicability of the assay was evaluated with clinical samples consisting of semen and organ specimens from experimentally infected animals.
Figures



References
-
- Abdelmagid O Y, Minocha H C, Collins J K, Chowdhury S I. Fine mapping of bovine herpesvirus-1 (BHV-1) glycoprotein D (gD) neutralizing epitopes by type-specific monoclonal antibodies and sequence comparison with BHV-5 gD. Virology. 1995;206:242–253. - PubMed
-
- Bartha A, Hajdu G, Aldasi P, Paczolay G. Occurrence of encephalitis caused by infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus in calves in Hungary. Acta Vet Hung. 1969;19:145–151. - PubMed
-
- Carrillo B J, Pospischil A, Dahme E. Pathology of bovine viral necrotizing encephalitis in Argentina. Zentbl Veterinarmed B. 1983;30:161–168. - PubMed
-
- Dietrich R A. Respiratory viruses. In: Dietrich R A, editor. Alaskan wildlife diseases. Fairbanks: University of Alaska; 1981. pp. 28–29.
-
- Dinter Z. In: Diagnostic virology. Moreno-Lopez G, editor. Uppsala: Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences; 1989. pp. 95–110.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

