Relatedness analyses of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates from Mexican patients with AIDS-associated histoplasmosis by using histoplasmin electrophoretic profiles and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA patterns
- PMID: 10203495
- PMCID: PMC84786
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.5.1404-1408.1999
Relatedness analyses of Histoplasma capsulatum isolates from Mexican patients with AIDS-associated histoplasmosis by using histoplasmin electrophoretic profiles and randomly amplified polymorphic DNA patterns
Abstract
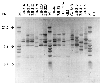
The present paper analyzes the histoplasmin electrophoretic profiles and the randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) patterns of the fungus Histoplasma capsulatum isolated from Mexican patients with AIDS-associated histoplasmosis. Clinical isolates from Guatemala, Colombia, and Panama, as well as H. capsulatum isolates from different sources in nature, were also processed. All histoplasmin samples shared four antigenic fractions of 200, 49, 10.5, and 8.5 kDa in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). According to their percentage of relatedness, based on SDS-PAGE histoplasmin electrophoretic image analysis, H. capsulatum isolates were divided in two groups: group A contained all AIDS-associated isolates studied and two human reference strains from Mexican histoplasmosis patients without AIDS; group B included bat guano, infected bat, and cock excreta isolates from the State of Guerrero, Mexico, plus three human histoplasmosis strains from Guatemala, Panama, and Colombia. Polymorphic DNA patterns evaluated by RAPD-PCR showed three major bands of 4.4, 3.2, and 2.3 kb in most H. capsulatum isolates studied. Four groups were related by DNA polymorphisms: group I was formed by most of the AIDS-associated H. capsulatum isolates studied, one human histoplasmosis strain from Colombia, two human reference strains from Mexican patients without AIDS, and one human histoplasmosis strain from Guatemala. Group II consisted of only a single strain from Panama. Group III included three strains: one from a Mexican patient with AIDS and two isolated from nature in Guerrero (cock excreta and bat guano). The last, group IV, consisted of only one strain isolated from an infected bat, captured in Guerrero. A tight relationship between phenotypic and genotypic characterization was observed, and both analyses could be useful tools for typing H. capsulatum from different sources and geographic origins.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Molecular typing of Histoplasma capsulatum isolated from infected bats, captured in Mexico.Fungal Genet Biol. 2000 Aug;30(3):207-12. doi: 10.1006/fgbi.2000.1219. Fungal Genet Biol. 2000. PMID: 11035942
-
Analyses of the genetic diversity and population structures of Histoplasma capsulatum clinical isolates from Mexico, Guatemala, Colombia and Argentina, using a randomly amplified polymorphic DNA-PCR assay.Epidemiol Infect. 2019 Jan;147:e204. doi: 10.1017/S0950268819000931. Epidemiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 31364543 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of Histoplasma capsulatum strains in Brazil.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005 Sep 1;45(3):443-9. doi: 10.1016/j.femsim.2005.05.018. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16055317
-
The importance of molecular analyses for understanding the genetic diversity of Histoplasma capsulatum: an overview.Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014 Jan-Mar;31(1):11-5. doi: 10.1016/j.riam.2013.09.013. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Rev Iberoam Micol. 2014. PMID: 24252830 Review.
-
[Disseminated histoplasmosis due to Histoplasma capsulatum in a patient with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)].Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1987 Aug 29;117(35):1289-96. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1987. PMID: 3313689 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The use of genetic markers in the molecular epidemiology of histoplasmosis: a systematic review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016 Jan;35(1):19-27. doi: 10.1007/s10096-015-2508-5. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 26589702
-
Development of specific sequence-characterized amplified region markers for detecting Histoplasma capsulatum in clinical and environmental samples.J Clin Microbiol. 2012 Mar;50(3):673-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.05271-11. Epub 2011 Dec 21. J Clin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22189121 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic diversity of Histoplasma capsulatum strains isolated from soil, animals, and clinical specimens in Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil, by a PCR-based random amplified polymorphic DNA assay.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Dec;39(12):4487-94. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.12.4487-4494.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11724867 Free PMC article.
-
Disseminated histoplasmosis from western Mexico-rethinking our geographic distribution of endemic fungal species: a case report and review of literature.J Med Case Rep. 2024 Nov 8;18(1):540. doi: 10.1186/s13256-024-04856-x. J Med Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39511652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histoplasma capsulatum Isolated from Tadarida brasiliensis Bats Captured in Mexico Form a Sister Group to North American Class 2 Clade.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Jun 30;7(7):529. doi: 10.3390/jof7070529. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baturen B, Bikandi J, San Millán R, Morangues M D, Regulez P, Quindós G, Pontón J. Variability in expression of antigens responsible for serotype specificity in Candida albicans. Microbiology. 1995;141:1535–1543. - PubMed
-
- Carter D A, Burt A, Taylor J W, Koening G L, Dechairo B M, White T J. A set of electrophoretic molecular markers for strain typing and population genetic studies of Histoplasma capsulatum. Electrophoresis. 1997;18:1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Casanova-Cardiel L J, Ruíz-Ordaz I. Histoplasma capsulatum en sangre periférica de pacientes con SIDA. Informe de cuatro casos con elevación de deshidrogenasa láctica. Rev Investig Clin. 1993;45:67–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

