Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis used to investigate genetic diversity of Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates in Australia shows differences between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal isolates
- PMID: 10203516
- PMCID: PMC84820
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.5.1524-1531.1999
Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis used to investigate genetic diversity of Haemophilus influenzae type b isolates in Australia shows differences between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal isolates
Abstract
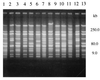
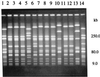
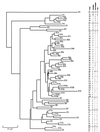
We used pulsed-field gel electrophoresis to study the epidemiology and population structure of Haemophilus influenzae type b. DNAs from 187 isolates recovered between 1985 and 1993 from Aboriginal children (n = 76), non-Aboriginal children (n = 106), and non-Aboriginal adults (n = 5) in urban and rural regions across Australia were digested with the SmaI restriction endonuclease. Patterns of 13 to 17 well-resolved fragments (size range, approximately 8 to 500 kb) defining 67 restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) types were found. Two types predominated. One type (n = 37) accounted for 35 (46%) of the isolates from Aboriginals and 2 (2%) of the isolates from non-Aboriginals, and the other type (n = 41) accounted for 2 (3%) of the isolates from Aboriginals and 39 (35%) of the isolates from non-Aboriginals. Clustering revealed seven groups at a genetic distance of approximately 50% similarity in a tree-like dendrogram. They included two highly divergent groups representing 50 (66%) isolates from Aboriginals and 6 (5%) isolates from non-Aboriginals and another genetically distinct group representing 7 (9%) isolates from Aboriginals and 81 (73%) isolates from non-Aboriginals. The results showed a heterogeneous clonal population structure, with the isolates of two types accounting for 42% of the sample. There was no association between RFLP type and the diagnosis of meningitis or epiglottitis, age, sex, date of collection, or geographic location, but there was a strong association between the origin of isolates from Aboriginal children and RFLP type F2a and the origin of isolates from non-Aboriginal children and RFLP type A8b. The methodology discriminated well among the isolates (D = 0.91) and will be useful for the monitoring of postvaccine isolates of H. influenzae type b.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Global genetic structure and molecular epidemiology of encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae.Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jan-Feb;12(1):75-111. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.1.75. Rev Infect Dis. 1990. PMID: 1967849
-
Comparative molecular analysis of Haemophilus influenzae isolates from young children with acute lower respiratory tract infections and meningitis in Hanoi, Vietnam.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 May;43(5):2474-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.5.2474-2476.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15872287 Free PMC article.
-
Use of automated riboprinter and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for epidemiological studies of invasive Haemophilus influenzae in Taiwan.J Med Microbiol. 2001 Mar;50(3):277-283. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-3-277. J Med Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11232775
-
The epidemiology and prevention of Haemophilus influenzae infections in Australian aboriginal children.J Paediatr Child Health. 1992 Oct;28(5):354-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1992.tb02691.x. J Paediatr Child Health. 1992. PMID: 1389445 Review. No abstract available.
-
Molecular epidemiology of Haemophilus influenzae type b.Pediatrics. 1990 Apr;85(4 Pt 2):636-42. Pediatrics. 1990. PMID: 2179853 Review.
Cited by
-
Chlamydia pneumoniae is genetically diverse in animals and appears to have crossed the host barrier to humans on (at least) two occasions.PLoS Pathog. 2010 May 20;6(5):e1000903. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000903. PLoS Pathog. 2010. PMID: 20502684 Free PMC article.
-
Typing of nonencapsulated haemophilus strains by repetitive-element sequence-based PCR using intergenic dyad sequences.J Clin Microbiol. 2003 Aug;41(8):3473-80. doi: 10.1128/JCM.41.8.3473-3480.2003. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. PMID: 12904341 Free PMC article.
-
Limited genetic diversity of recent invasive isolates of non-serotype b encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;40(4):1264-70. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1264-1270.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11923343 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of non-type B Haemophilus influenzae strains isolated from patients with invasive disease. The HI Study Group.J Clin Microbiol. 2000 Dec;38(12):4649-52. doi: 10.1128/JCM.38.12.4649-4652.2000. J Clin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11101614 Free PMC article.
-
High rates of recombination in otitis media isolates of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae.Infect Genet Evol. 2003 May;3(1):57-66. doi: 10.1016/s1567-1348(02)00152-1. Infect Genet Evol. 2003. PMID: 12797973 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbeit R D, Dunn R, Maslow J, Goldstein R, Musser J M. Program and abstracts of the 30th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. Washington, D.C: American Society for Microbiology; 1990. Resolution of evolutionary divergence and epidemiologic relatedness among H. influenzae type b (Hib) by pulse field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), abstr. 1144; p. 277.
-
- Armstrong, J. S., A. J. Gibbs, R. Peakall, and G. Weiller. 1994. The RAPDistance package. [Online.] Australian National University. ftp://life.anu.edu.au/pub/software/RAPDistance or http://life.anu.edu.au/molecular/software/rapd.html. [October 1998, last date accessed.]
-
- Bautsch W. Bacterial genome mapping by two-dimensional pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (2D-PFGE) Methods Mol Biol. 1992;12:185–201. - PubMed
-
- Butler P, Moxon E R. A physical map of the genome of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136:2333–2342. - PubMed
-
- Curran R, Hardie K R, Towner K J. Analysis by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of insertion mutations in the transferrin-binding system of Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Med Microbiol. 1994;41:120–126. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

