Identification of glucoside and carboxyl-linked glucuronide conjugates of mycophenolic acid in plasma of transplant recipients treated with mycophenolate mofetil
- PMID: 10204993
- PMCID: PMC1565876
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702399
Identification of glucoside and carboxyl-linked glucuronide conjugates of mycophenolic acid in plasma of transplant recipients treated with mycophenolate mofetil
Abstract
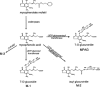
1. Mycophenolic acid (MPA), is primarily metabolized in the liver to 7-O-MPA-beta-glucuronide (MPAG). Using RP-h.p.l.c. we observed three further MPA metabolites, M-1, M-2, M-3, in plasma of transplant recipients on MMF therapy. To obtain information on the structure and source of these metabolites: (A) h.p.l.c. fractions containing either metabolite or MPA were collected and analysed by tandem mass spectrometry; (B) the metabolism of MPA was studied in human liver microsomes in the presence of UDP-glucuronic acid, UDP-glucose or NADPH; (C) hydrolysis of metabolites was investigated using beta-glucosidase, beta-glucuronidase or NaOH; (D) cross-reactivity of each metabolite was tested in an immunoassay for MPA (EMIT). 2. Mass spectrometry of M-1, M-2, MPA and MPAG in the negative ion mode revealed molecular ions of m/z 481, m/z 495, m/z 319 and m/z 495 respectively. 3. Incubation of microsomes with MPA and UDP-glucose produced M-1, with MPA and UDP-glucuronic acid MPAG and M-2 were formed, while with MPA and NADPH, M-3 was observed. 4. Beta-Glucosidase hydrolysed M-1 completely. Beta-Glucuronidase treatment led to a complete disappearance of MPAG whereas the amount of M-2 was reduced by approximately 30%. Only M-2 was labile to alkaline treatment. 5. M-2 and MPA but not M-1 and MPAG cross-reacted in the EMIT assay. 6. These results suggest that: (i) M-1 is the 7-OH glucose conjugate of MPA; (ii) M-2 is the acyl glucuronide conjugate of MPA; (iii) M-3 is derived from the hepatic CYP450 system.
Figures



References
-
- BRIGGS W.A., CHOI M.J., SCHEEL P.J., JR Successful mycophenolate mofetil treatment of glomerular disease. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1998;31:213–217. - PubMed
-
- BULLINGHAM R.E.S., NICHOLLS A.J., KAMM B.R. Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1998;34:429–455. - PubMed
-
- DICKINSON R.G., HOOPER W.D., EADIE M.J. pH-dependent rearrangement of the biosynthetic ester glucuronide of valproic acid to β-glucuronidase-resistant forms. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1984;12:247–252. - PubMed
-
- ENK A.H., KNOP J. Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with mycophenolate mofetil [letter] Lancet. 1997;350:494. - PubMed
-
- HALEY C.J., JAKLITSCH A., MCGOWAN B., WIEDER-BUNGER T., KAMPE T., ALEXANDER S.Feasibility of an Emit assay for mycophenolic acid in plasma Ther. Drug Monit. 199517431et al
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

