Electrophysiological studies on the postnatal development of the spinal antinociceptive effects of the delta opioid receptor agonist DPDPE in the rat
- PMID: 10204998
- PMCID: PMC1565889
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702418
Electrophysiological studies on the postnatal development of the spinal antinociceptive effects of the delta opioid receptor agonist DPDPE in the rat
Abstract
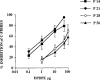
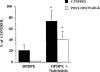
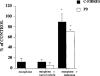
1. The antinociceptive effects of the delta opioid receptor selective agonist, DPDPE [(D-Pen2,D-Pen5)-enkephalin] was studied in rats aged postnatal day (P) 14, P21, P28 and P56. 2. Antinociceptive effects of DPDPE were measured as percentage inhibition of the C-fibre evoked response and post-discharge of dorsal horn neurones evoked by peripheral electrical stimulation. DPDPE was administered by topical application, akin to intrathecal injection. 3. DPDPE (0.1-100 microg) produced dose-related inhibitions at all ages; these inhibitions were reversed by 5 microg of the opioid antagonist naloxone. 4. The dose-response curves for C-fibre evoked response and post-discharge of the neurones were not different in rats aged P14 and P21. DPDPE was significantly more potent at P14 and P21 compared with its inhibitory effects on these responses at P28 and P56. 5. DPDPE produced minor inhibitions of the A-fibre evoked response of the neurones at P14, P21, P28 and P56, suggesting that the inhibitory effects of DPDPE are mediated via presynaptic receptors on the terminals of C-fibre afferents. 6. Since spinal delta opioid receptor density changes little over this period, the increased antinociceptive potency of DPDPE in the rat pups compared with the adult is likely to be due to post-receptor events, or in developmental changes in the actions of other transmitter/receptor systems within the spinal cord.
Figures
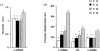


Similar articles
-
Differential effects of intrathecally administered delta and mu opioid receptor agonists on formalin-evoked nociception and on the expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Jan;284(1):378-87. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9435201
-
Delta opioid receptor enhancement of mu opioid receptor-induced antinociception in spinal cord.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Jun;285(3):1181-6. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9618421
-
Antinociception and delta-1 opioid receptors in the rat spinal cord: studies with intrathecal 7-benzylidenenaltrexone.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Sep;274(3):1317-24. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. PMID: 7562504
-
Evidence for delta opioid receptor subtypes in rat spinal cord: studies with intrathecal naltriben, cyclic[D-Pen2, D-Pen5] enkephalin and [D-Ala2, Glu4]deltorphin.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Aug;266(2):820-8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993. PMID: 8394918
-
Spinal opioid delta antinociception in the mouse: mediation by a 5'-NTII-sensitive delta receptor subtype.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):518-25. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992. PMID: 1310737
Cited by
-
δ-opioid receptor function in the dorsal striatum plays a role in high levels of ethanol consumption in rats.J Neurosci. 2012 Mar 28;32(13):4540-52. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5345-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22457501 Free PMC article.
-
Opioid receptor signaling throughout ontogeny: Shaping neural and behavioral trajectories.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025 Mar;170:106033. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2025.106033. Epub 2025 Jan 31. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2025. PMID: 39894419 Review.
-
Endogenous Opioids and Their Role in Stem Cell Biology and Tissue Rescue.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 30;23(7):3819. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073819. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409178 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ABBOTT F.V., GUY E.R. Effects of morphine, pentobarbital and amphetamine on formalin-induced behaviours in infant rats: sedation versus specific suppression of pain. Pain. 1995;62:303–312. - PubMed
-
- ATTALI B., SAYA D., VOGEL Z. Pre- and postnatal development of opioid receptor subtypes in rat spinal cord. Dev. Brain Res. 1990;53:97–102. - PubMed
-
- BARR G.A.Behavioural effects of opiates during development Development of the central nervous system: Effects of alcohol and opiates 1992New York: Wiley-Liss; 221–254.ed. Miller, M.W. pp
-
- BICKNELL H.R., BEAL J.A. Aconal and dendritic development of substantia gelatinosa neurones in the lumbosacral spinal cord of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984;226:508–522. - PubMed
-
- BLASS E.M., CRAMER C.P., FANSELOW M.S. The development of morphine-induced antinociception in neonatal rats : a comparison of forepaw, hindpaw, and tail retraction from a thermal stimulus. Pharm. Biochem Behav. 1993;44:643–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

