Inhibition by simvastatin, but not pravastatin, of glucose-induced cytosolic Ca2+ signalling and insulin secretion due to blockade of L-type Ca2+ channels in rat islet beta-cells
- PMID: 10205010
- PMCID: PMC1565875
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702397
Inhibition by simvastatin, but not pravastatin, of glucose-induced cytosolic Ca2+ signalling and insulin secretion due to blockade of L-type Ca2+ channels in rat islet beta-cells
Abstract
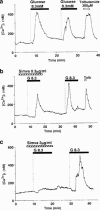
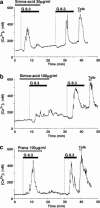
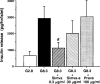
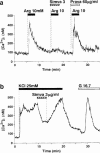
1. Hypercholesterolaemia often occurs in patients with type 2 diabetes, who therefore encounter administration of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. Alteration of pancreatic beta-cell function leading to an impaired insulin secretory response to glucose plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Therefore, it is important to examine the effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on beta-cell function. 2. Cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) plays a central role in the regulation of beta-cell function. The present study examined the effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors on the glucose-induced [Ca2+]i signalling and insulin secretion in rat islet beta-cells. 3. Simvastatin, a lipophilic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, at 0.1-3 microg ml(-1) concentration-dependently inhibited the first phase increase and oscillation of [Ca2+]i induced by 8.3 mM glucose in single beta-cells. The less lipophilic inhibitor, simvastatin-acid, inhibited the first phase [Ca2+]i increase but was two orders of magnitude less potent. The hydrophilic inhibitor, pravastatin (100 microg ml(-1), was without effect on [Ca2+]i. 4. Simvastatin (0.3 microg ml(-1)), more potently than simvastatin-acid (30 microg ml(-1)), inhibited glucose-induced insulin secretion from islets, whereas pravastatin (100 microg ml(-1)) had no effect. 5. Whole-cell patch clamp recordings demonstrated a reversible inhibition of the beta-cell L-type Ca2+ channels by simvastatin, but not by pravastatin. Simvastatin also inhibited the [Ca2+]i increases by L-arginine and KCl, agents that act via opening of L-type Ca2+ channels. 6. In conclusion, lipophilic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors can inhibit glucose-induced [Ca2+]i signalling and insulin secretion by blocking L-type Ca2+ channels in beta-cells, and their inhibitory potencies parallel their lipophilicities. Precaution should be paid to these findings when HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors are used clinically, particularly in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Figures



References
-
- ALBERTS A.W. Discovery, biochemistry and biology of lovastatin. Am. J. Cardiol. 1988;62:10J–15J. - PubMed
-
- APPEL S., RUFENACHT T., KALAFSKY G., TETZLOFF W., KALLAY Z., HITZENBERGER G., KUTZ K. Lack of interaction between fluvastatin and oral hypoglycemic agents in healthy subjects and in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Cardiol. 1995;76:29A–32A. - PubMed
-
- ASHCROFT F.M., RORSMAN P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic β-cell. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1989;54:87–143. - PubMed
-
- BERGSTEN P. Slow and fast oscillations of cytoplasmic Ca2+ in pancreatic islets correspond to pulsatile insulin release. Am. J. Physiol. 1995;268:E282–E287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

