Mycoplasma pneumoniae-associated bronchiolitis causing severe restrictive lung disease in adults: report of three cases and literature review
- PMID: 10208228
- PMCID: PMC7094532
- DOI: 10.1378/chest.115.4.1188
Mycoplasma pneumoniae-associated bronchiolitis causing severe restrictive lung disease in adults: report of three cases and literature review
Abstract
Study objectives: To characterize adult Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced bronchiolitis requiring hospitalization.
Design: We encountered an adult patient with severe bronchiolitis in the absence of pneumonia due to M. pneumoniae. To determine the relative frequency of such a condition, we retrospectively reviewed the medical records of adults over a 4-year period with a hospital discharge diagnosis of "bronchiolitis" from a university hospital.
Setting: University Hospital of the University of Colorado Health Sciences Center, Denver, CO.
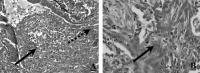
Study subjects: From 1994 to 1998, 10 adult inpatients were identified with a diagnosis of bronchiolitis. There were two with respiratory bronchiolitis, one with panbronchiolitis, one patient with bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP), and six with acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. Including the initial patient, three had a definitive clinical diagnosis of Mycoplasma-associated bronchiolitis.
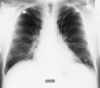
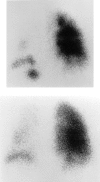
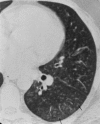
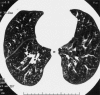
Results: The three adult patients with bronchiolitis due to M. pneumoniae are unusual because they occurred in the absence of radiographic features of a lobar or patchy alveolar pneumonia. Hospital admission was occasioned by the severity of symptoms and gas exchange abnormalities. One patient had bronchiolitis as well as organizing pneumonia (BOOP) that responded favorably to corticosteroid treatment. The other two had high-resolution CT findings diagnostic of an acute inflammatory bronchiolitis. One of the patients with inflammatory bronchiolitis had an unusual pattern of marked ventilation and perfusion defects localized predominantly to the left lung. All three had restrictive ventilatory impairment on physiologic testing.
Conclusions: In adults, Mycoplasma-associated bronchiolitis without pneumonia is rarely reported, but in hospitalized patients, it may be more common than expected and may be associated with severe physiologic disturbances.
Figures
References
-
- Leong MA, Nachajon R, Ruchelli E. Bronchitis obliterans due to Mycoplasma pneumonia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1997;23:375–381. - PubMed
-
- Kawata K, Sumino Y, Kikuchi Y. Two cases of Mycoplasma pneumoniae with cavity formation. Jpn J Med. 1978;17:144–147.
-
- Stokes D, Sigler A, Khouri NF. Unilateral hyperlucent lung (Swyer-James syndrome) after severe Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978;117:145–152. - PubMed
-
- Solanki DL, Berdoff RL. Severe mycoplasma pneumonia with pleural effusions in a patient with sickle cell-hemoglobin C (SC) disease—case report and review of the literature. Am J Med. 1979;66:707–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

