Increased interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) levels produced in vitro by alloactivated T lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis and Raynaud's phenomenon
- PMID: 10209521
- PMCID: PMC1905213
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00842.x
Increased interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) levels produced in vitro by alloactivated T lymphocytes in systemic sclerosis and Raynaud's phenomenon
Abstract
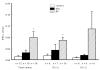
The aim of the present study was to analyse the in vitro proliferation and cytokine production by alloantigen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) obtained from patients affected by systemic sclerosis (SSc) and patients with Raynaud's phenomenon (RP). In SSc patients the proliferation of PBMC stimulated in vitro with alloantigens was significantly increased compared with healthy subjects, while no differences were observed for RP patients. Lymphocytes from SSc patients also produced larger amounts of IFN-gamma compared with healthy controls. However, patients with clinically active disease had lower IFN-gamma levels than those found in clinically stable patients. Patients affected by RP showed significantly higher levels of IFN-gamma than healthy subjects. Analysis at the clonal level of the lymphocyte subsets involved in alloantigen stimulation in one patient affected by active SSc, and one subject with RP confirmed the results obtained using PBMC. In particular, in the RP patient but not in the SSc patient, we observed a population of CD4+ T cells which proliferated to alloantigens in vitro and produced high levels of IFN-gamma. We suggest that T lymphocytes producing high levels of IFN-gamma might play a protective role in RP patients and in established scleroderma.
Figures
References
-
- Kahaleh B. Immunologic aspects of scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1993;5:760–5. - PubMed
-
- Postlethwaite AE. Connective tissue metabolism including cytokines in scleroderma. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 1993;5:766–72. - PubMed
-
- Prescott RJ, Freemont AJ, Jones CJP, Hoyland J, Fiending P. Sequential dermal microvascular and perivascular changes in the development of scleroderma. J Pathol. 1992;166:255–63. - PubMed
-
- White B. Immunopathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 1996;22:695–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials