Genetic dissection of behavior: modulation of locomotion by light in the Drosophila melanogaster larva requires genetically distinct visual system functions
- PMID: 10212293
- PMCID: PMC6782248
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-09-03337.1999
Genetic dissection of behavior: modulation of locomotion by light in the Drosophila melanogaster larva requires genetically distinct visual system functions
Abstract
The Drosophila larva modulates its pattern of locomotion when exposed to light. Modulation of locomotion can be measured as a reduction in the distance traveled and by a sharp change of direction when the light is turned on. When the light is turned off this change of direction, albeit significantly smaller than when the light is turned on, is still significantly larger than in the absence of light transition. Mutations that disrupt adult phototransduction disrupt a subset of these responses. In larvae carrying these mutations the magnitude of change of direction when the light is turned on is reduced to levels indistinguishable from that recorded when the light is turned off, but it is still significantly higher than in the absence of any light transition. Similar results were obtained when these responses were measured in strains where the larval photoreceptor neurons were ablated by mutations in the glass (gl) gene or by the targeted expression of the cell death gene head involution defective (hid). A mutation in the homeobox gene sine oculis (so) that ablates the larval visual system, or the targeted expression of the reaper (rpr) cell death gene, abolishes all responses to light detected as a change of direction. We propose the existence of an extraocular light perception that does not use the same phototransduction cascade as the adult photoreceptors. Our results indicate that this novel visual function depends on the blue-absorbing rhodopsin Rh1 and is specified by the so gene.
Figures
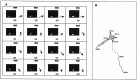
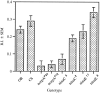


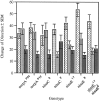


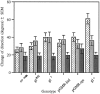
References
-
- Ashburner M. Drosophila: A laboratory handbook, pp 139–298. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; Cold Spring Harbor, NY: 1989. Developmental biology.
-
- Bloomquist BT, Shortridge RD, Schneuwly S, Perdew M, Montell C, Steller H, Rubin G, Pak WL. Isolation of a putative phospholipase C gene of Drosophila, norpA, and its role in phototransduction. Cell. 1988;54:723–733. - PubMed
-
- Bolwig N. Sense and sense organs of the anterior end of the house fly larvae. Vidensk Medd Dan Naturhist Foren. 1946;109:81–217.
-
- Campos AR, Lee KJ, Steller H. Establishment of neuronal connectivity during development of the Drosophila visual system. J Neurobiol. 1995;28:313–329. - PubMed
-
- Cheyette BNR, Green PJ, Martin K, Garren H, Hartenstein V, Zipursky SL. The Drosophila sine oculis locus encodes a homeodomain-containing protein required for the development of the entire visual system. Neuron. 1994;12:977–996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
