Catecholamine synthesis is mediated by tyrosinase in the absence of tyrosine hydroxylase
- PMID: 10212311
- PMCID: PMC6782225
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-09-03519.1999
Catecholamine synthesis is mediated by tyrosinase in the absence of tyrosine hydroxylase
Abstract
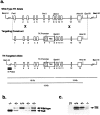
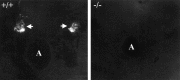
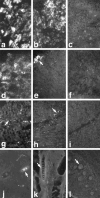
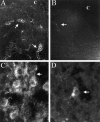
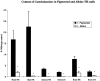
Catecholamine neurotransmitters are synthesized by hydroxylation of tyrosine to L-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-Dopa) by tyrosine hydroxylase (TH). The elimination of TH in both pigmented and albino mice described here, like pigmented TH-null mice reported previously (Kobayashi et al., 1995; Zhou et al., 1995), demonstrates the unequivocal requirement for catecholamines during embryonic development. Although the lack of TH is fatal, TH-null embryos can be rescued by administration of catecholamine precursors to pregnant dams. Once born, TH-null pups can survive without further treatment until weaning. Given the relatively rapid half-life of catecholamines, we expected to find none in postnatal TH-null pups. Despite the fact that the TH-null pups lack TH and have not been supplemented with catecholamine precursers, catecholamines are readily detected in our pigmented line of TH-null mice by glyoxylic acid-induced histofluorescence at postnatal day 7 (P7) and P15 and quantitatively at P15 in sympathetically innervated peripheral organs, in sympathetic ganglia, in adrenal glands, and in brains. Between 2 and 22% of wild-type catecholamine concentrations are found in these tissues in mutant pigmented mice. To ascertain the source of the catecholamine, we examined postnatal TH-null albino mice that lack tyrosinase, another enzyme that converts tyrosine to L-Dopa but does so during melanin synthesis. In contrast to the pigmented TH-null mice, catecholamine histofluorescence is undetectable in postnatal albino mutants, and the catecholamine content of TH-null pups lacking tyrosinase is 18% or less than that of TH-null mice with tyrosinase. Thus, these extraordinary circumstances reveal that tyrosinase serves as an alternative pathway to supply catecholamines.
Figures

References
-
- Beermann F, Schmid E, Ganss R, Schutz G, Ruppert S. Molecular characterization of the mouse tyrosinase gene: pigment cell-specific expression in transgenic mice. Pigm Cell Res. 1992;5:295–299. - PubMed
-
- Blaschko H. The specific action of l-dopa decarboxylase. J Physiol (Lond) 1939;96:50–51.
-
- De la Torre J. An improved approach to histofluorescence using the SPG method for tissue monoamines. J Neurosci Methods. 1980;3:1–5. - PubMed
-
- DeChamplain J, Malmfors T, Olson L, Sachs C. Ontogenesis of peripheral adrenergic neurons in the rat: pre- and postnatal observations. Acta Physiol Scand. 1970;80:276–288. - PubMed
-
- Eisenhofer G, Goldstein D, Stull R, Keiser H, Sunderland T, Murphy D, Kopin I. Simultaneous liquid chromatographic determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylglycol, catecholamines and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine in plasma, and their responses to monoamine oxidase inhibition. Clin Chem. 1986;32:2030–2033. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
