Cytochrome P450 isoform selectivity in human hepatic theobromine metabolism
- PMID: 10215755
- PMCID: PMC2014222
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.1999.00890.x
Cytochrome P450 isoform selectivity in human hepatic theobromine metabolism
Abstract
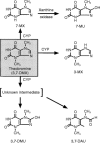
Aims: The plasma clearance of theobromine (TB; 3,7-dimethylxanthine) is known to be induced in cigarette smokers. To determine whether TB may serve as a model substrate for cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, or possibly other isoforms, studies were undertaken to identify the individual human liver microsomal CYP isoforms responsible for the conversion of TB to its primary metabolites.
Methods: The kinetics of formation of the primary TB metabolites 3-methylxanthine (3-MX), 7-methylxanthine (7-MX) and 3,7-dimethyluric acid (3,7-DMU) by human liver microsomes were characterized using a specific hplc procedure. Effects of CYP isoform-selective xenobiotic inhibitor/substrate probes on each pathway were determined and confirmatory studies with recombinant enzymes were performed to define the contribution of individual isoforms to 3-MX, 7-MX and 3,7-DMU formation.
Results: The CYP1A2 inhibitor furafylline variably inhibited (0-65%) 7-MX formation, but had no effect on other pathways. Diethyldithiocarbamate and 4-nitrophenol, probes for CYP2E1, inhibited the formation of 3-MX, 7-MX and 3,7-DMU by approximately 55-60%, 35-55% and 85%, respectively. Consistent with the microsomal studies, recombinant CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 exhibited similar apparent Km values for 7-MX formation and CYP2E1 was further shown to have the capacity to convert TB to both 3-MX and 3,7-DMU.
Conclusions: Given the contribution of multiple isoforms to 3-MX and 7-MX formation and the negligible formation of 3,7-DMU in vivo, TB is of little value as a CYP isoform-selective substrate in humans.
Figures


References
-
- Eaton DL, Gallagher EP, Bammler TK, Kunze KL. Role of cytochrome P4501A2 in chemical carcinogenesis: implications for human variability in expression and enzyme activity. Pharmacogenetics. 1995;5:259–274. - PubMed
-
- Guengerich FP. Metabolic activation of carcinogens. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;54:17–61. - PubMed
-
- Miners JO, McKinnon RA. Cytochrome P4501A. In: Levy RH, Thummel KE, Trager WF, Hansten PD, Eichelbaum M, editors. Metabolic Drug Interactions. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; (in press)
-
- McKinnon RA, Hall PM, Quattrochi LC, Tukey RH, McManus ME. Localization of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 mRNA in normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma by in situ hybridization. Hepatology. 1991;14:848–856. - PubMed
-
- Schweik H, Taylor JA, Kitareewan S, Linko P, Nagorney D, Goldstein JA. Expression of CYP1A1 and CYP1A2 genes in human liver. Pharmacogenetics. 1993;3:239–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

