Modulation of the gating of CIC-1 by S-(-) 2-(4-chlorophenoxy) propionic acid
- PMID: 10217531
- PMCID: PMC1565926
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702459
Modulation of the gating of CIC-1 by S-(-) 2-(4-chlorophenoxy) propionic acid
Abstract
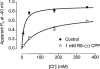
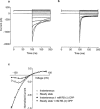
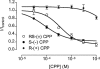
1. Using whole-cell patch-clamping and Sf-9 cells expressing the rat skeletal muscle chloride channel, rCIC-1, the cellular mechanism responsible for the myotonic side effects of clofibrate derivatives was examined. 2. RS-(+/-) 2-(4-chlorophenoxy)propionic acid (RS-(+/-) CPP) and its S-(-) enantiomer produced pronounced effects on CIC-1 gating. Both compounds caused the channels to deactivate more rapidly at hyperpolarizing potentials, which showed as a decrease in the time constants of both the fast and slow deactivating components of the whole cell currents. Both compounds also produced a concentration-dependent shift in the voltage dependence of channel apparent open probability to more depolarizing potentials, with an EC50 of 0.79 and 0.21 mM for the racemate and S-(-) enantiomer respectively. R-(+) CPP at similar concentrations had no effect on gating. RS-(+/-) CPP did not block the passage of Cl- through the pore of rCIC-1. 3. CIC-1 is gated by Cl- binding to a site within an access channel and S-(-) CPP alters gating of the channel by decreasing the affinity of this binding site for Cl-. Comparison of the EC50 for RS-(+/-) CPP and S-(-) CPP indicates that R-(+) CPP can compete with the S-(-) enantiomer for the site but that it is without biological activity. 4. RS-(+/-) CPP produced the same effect on rCIC-1 gating when added to the interior of the cell and in the extracellular solution. 5. S-(-) CPP modulates the gating of CIC-1 to decrease the membrane Cl- conductance (GCl), which would account for the myotonic side effects of clofibrate and its derivatives.
Figures

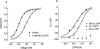

References
-
- ASTILL D.STJ., RYCHKOV G.Y., CLARKE J.D., HUGHES B.P., ROBERTS M.L., BRETAG A.H. Characteristics of skeletal muscle chloride channel ClC-1 and point mutant R304E expressed in Sf-9 insect cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1996;1280:178–186. - PubMed
-
- BALDWIN J., WITIAK D., FELLER D. Disposition of clofibrate in the rat: Acute and chronic administration. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1980;29:3143–3154. - PubMed
-
- BARRY P.H. JPCalc, a software package for calculating liquid junction potential corrections in patch-clamp, intracellular, epithelial and bilayer measurements and for correcting junction potential measurements. J. Neurosci. Meth. 1994;51:107–116. - PubMed
-
- BERWICK P. 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid poisoning in man. JAMA. 1970;214:1114–1117. - PubMed
-
- BETTONI G., LOIODICE F., TORTORELLA V., CONTE CAMERINO D., MAMBRINI M., FERRANNINI E., BRYANT S.H. Stereospecificity of the chloride ion channel: The action of chiral clofibric acid analogues. J. Med. Chem. 1987;30:1267–1270. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

