GABA(B) receptor isoforms GBR1a and GBR1b, appear to be associated with pre- and post-synaptic elements respectively in rat and human cerebellum
- PMID: 10217533
- PMCID: PMC1565927
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0702460
GABA(B) receptor isoforms GBR1a and GBR1b, appear to be associated with pre- and post-synaptic elements respectively in rat and human cerebellum
Abstract
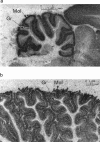
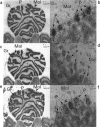
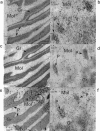
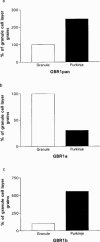
1. Metabotropic gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors, GABA(B), are coupled through G-proteins to K+ and Ca2+ channels in neuronal membranes. Cloning of the GABAB receptor has not uncovered receptor subtypes, but demonstrated two isoforms, designated GBR1a and GBR1b, which differ in their N terminal regions. In the rodent cerebellum GABA(B) receptors are localized to a greater extent in the molecular layer, and are reported to exist on granule cell parallel fibre terminals and Purkinje cell (PC) dendrites, which may represent pre- and post-synaptic receptors. 2. The objective of this study was to localize the mRNA splice variants, GBR1a and GBR1b for GABA(B) receptors in rat cerebellum, for comparison with the localization in human cerebellum using in situ hybridization. 3. Receptor autoradiography was performed utilizing [3H]-CGP62349 to localize GABA(B) receptors in rat and human cerebellum. Radioactively labelled oligonucleotide probes were used to localize GBR1a and GBR1b, and by dipping slides in photographic emulsion, silver grain images were obtained for quantification at the cellular level. 4. Binding of 0.5 nM [3H]-CGP62349 demonstrated significantly higher binding to GABA(B) receptors in the molecular layer than the granule cell (GC) layer of rat cerebellum (molecular layer binding 200+/-11% of GC layer; P<0.0001). GBR1a mRNA expression was found to be predominantly in the GC layer (PC layer grains 6+/-6% of GC layer grains; P<0.05), and GBR1b expression predominantly in PCs (PC layer grains 818+/-14% of GC layer grains; P<0.0001). 5. The differential distribution of GBR1a and GBR1b mRNA splice variants for GABA(B) receptors suggests a possible association of GBR1a and GBR1b with pre- and post-synaptic elements respectively.
Figures

References
-
- ALBIN R.L., GILMAN S. Autoradiographic localisation of inhibitory and excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter receptors in human normal and olivopontocerebellar atrophy cerebellar cortex. Brain Res. 1990;522:37–45. - PubMed
-
- ANDRADE R., MALENKA R.C., NICOLL R.A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986;234:1261–1265. - PubMed
-
- BETTLER B., KAUPMANN K., BOWERY N.G. GABAB receptors: drugs meet clones. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1998;8:345–350. - PubMed
-
- BILLINTON A., UPTON N., BETTLER B., BOWERY N.G. Differential expression of GABAB receptor GBR1a and GBR1b splice variants in human and rat cerebellar cortex. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1998;358 Suppl. 1:R148.
-
- BITTIGER H., BELLOUIN C., FROESTL W., HEID J., SCHMUTZ M., STAMPF P. [3H]CGP62349: a new potent GABAB receptor antagonist radioligand. Pharmacol. Rev. Commun. 1996;8:97–98.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

