Rapid pole-to-pole oscillation of a protein required for directing division to the middle of Escherichia coli
- PMID: 10220403
- PMCID: PMC21801
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.96.9.4971
Rapid pole-to-pole oscillation of a protein required for directing division to the middle of Escherichia coli
Abstract
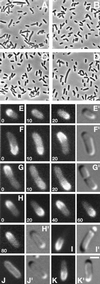
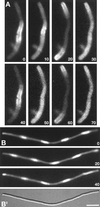
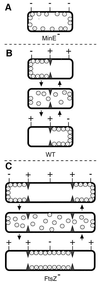
Accurate placement of the division septum at the midpoint of Escherichia coli cells requires the combined action of a general division inhibitor (MinC), a site-specific suppressor of division inhibition (MinE), and an ATPase (MinD) that is required for proper functioning of both MinC and MinE. We previously showed that a functional MinE-Gfp fusion accumulates in a ring structure at/near the middle of cells. Here we show that functional Gfp-MinD accumulates alternately in either one of the cell halves in what appears to be a rapidly oscillating membrane association-dissociation cycle imposed by MinE. The results indicate that MinD represents a novel type of dynamic cellular element in bacteria, with multiple roles in directing the division apparatus to the middle of the cell.
Figures

Comment in
-
Bacterial cell division: a moveable feast.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999 May 25;96(11):5891-3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.11.5891. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999. PMID: 10339512 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

