Examination of physiological and molecular factors involved in enhanced solvent production by clostridium beijerinckii BA101
- PMID: 10224036
- PMCID: PMC91333
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.65.5.2269-2271.1999
Examination of physiological and molecular factors involved in enhanced solvent production by clostridium beijerinckii BA101
Abstract
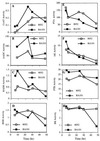
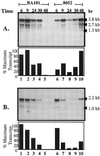
The specific activities and the mRNA expression levels associated with coenzyme A transferase, acetoacetate decarboxylase, and butyraldehyde dehydrogenase were elevated in hyper-solvent-producing Clostridium beijerinckii BA101 during the exponential growth phase. The increase in expression of the sol operon and associated enzyme activities may be responsible for enhanced solvent production by C. beijerinckii BA101.
Figures
References
-
- Andersch W, Bahl H, Gottschalk G. Level of enzymes involved in acetate, butyrate, acetone and butanol formation by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1983;18:327–332.
-
- Blaschek H P. Approaches to making the food processing industry more environmentally friendly. Trends Food Sci Technol. 1991;3:107–110.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

