Distinct kainate receptor phenotypes in immature and mature mouse cerebellar granule cells
- PMID: 10226148
- PMCID: PMC2269313
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0051z.x
Distinct kainate receptor phenotypes in immature and mature mouse cerebellar granule cells
Abstract
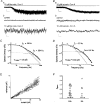
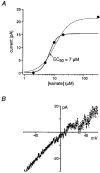
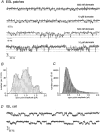
1. Although glutamate receptors have been shown to be involved in neuronal maturation, a developmental role for kainate-type receptors has not been described. In addition, the single-channel properties of native kainate receptors have not been studied in situ. We have characterized the electrophysiological properties of native kainate receptors of granule cell neurons at two distinct stages in postnatal development, using whole-cell and outside-out patch-clamp recordings in acute cerebellar slices. 2. Kainate-type currents were detected in both immature and mature granule cells. However, noise analysis showed that the apparent unitary conductance of kainate-type channels is significantly higher in proliferating than post-migratory granule cells. The conductance and rectification behaviour of the channels in immature granule cells indicate that they contain unedited GluR5 and GluR6 subunits and are likely to be calcium permeable. 3. Single-channel kainate-type currents were observed in outside-out patches from proliferating granule cells in the external germinal layer. The kinetic behaviour of kainate receptors in immature cells was complex. Openings to multiple conductance levels were observed, although our analysis indicates that the channels spend most of their open time in a 4 pS state.
Figures

Comment in
-
Developing roles for kainate receptors in the cerebellum.J Physiol. 1999 May 15;517 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):1. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0001z.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10226142 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
High-affinity kainate-type ion channels in rat cerebellar granule cells.J Physiol. 1998 Jul 15;510 ( Pt 2)(Pt 2):401-20. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.401bk.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9705992 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of non-NMDA receptor channels in type-2 astrocytes and granule cells from rat cerebellum.J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):95-114. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020052. J Physiol. 1994. PMID: 7514667 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for more than one type of non-NMDA receptor in outside-out patches from cerebellar granule cells of the rat.J Physiol. 1993 Apr;463:193-226. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019591. J Physiol. 1993. PMID: 7504104 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of RNA editing and subunit co-assembly single-channel properties of recombinant kainate receptors.J Physiol. 1996 Apr 1;492 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):129-42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021295. J Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8730589 Free PMC article.
-
Noise and single channels activated by excitatory amino acids in rat cerebellar granule neurones.J Physiol. 1988 Jun;400:189-222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017117. J Physiol. 1988. PMID: 2458453 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Kainate receptors expressed by a subpopulation of developing nociceptors rapidly switch from high to low Ca2+ permeability.J Neurosci. 2001 Jul 1;21(13):4572-81. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-13-04572.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11425885 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of GluR6 kainate receptor subunit in granular layer of weaver mouse cerebellum.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009 Apr;116(4):417-22. doi: 10.1007/s00702-009-0199-8. Epub 2009 Mar 5. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2009. PMID: 19263192
-
Lead induces similar gene expression changes in brains of gestationally exposed adult mice and in neurons differentiated from mouse embryonic stem cells.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 19;8(11):e80558. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080558. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24260418 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental changes in AMPA and kainate receptor-mediated quantal transmission at thalamocortical synapses in the barrel cortex.J Neurosci. 2005 May 25;25(21):5259-71. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0827-05.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15917466 Free PMC article.
-
Functional diversity and developmental changes in rat neuronal kainate receptors.J Physiol. 2001 Apr 15;532(Pt 2):411-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0411f.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11306660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altman J. Postnatal development of the cerebellar cortex in the rat. I. The external germinal layer and the transitional layer. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1972;145:353–398. - PubMed
-
- Bading H, Ginty DD, Greenberg ME. Regulation of gene expression in hippocampal neurons by distinct calcium signaling pathways. Science. 1993;260:181–186. - PubMed
-
- Belcher SM, Howe JR. Characterization of RNA editing of the glutamate-receptor subunits GluR5 and GluR6 in granule cells during cerebellar development. Molecular Brain Research. 1997;52:130–138. - PubMed
-
- Bessho Y, Nawa H, Nakanishi S. Selective upregulation of an NMDA receptor subunit mRNA in cultured cerebellar granule cells by K+-induced depolarization and NMDA treatment. Neuron. 1994;12:87–95. - PubMed
-
- Bettler B, Mulle C. Review: Neurotransmitter receptors II. AMPA and kainate receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1995;34:123–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

