Homologous and heterologous asynchronicity between identified alpha-, beta- and delta-cells within intact islets of Langerhans in the mouse
- PMID: 10226151
- PMCID: PMC2269319
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.0085z.x
Homologous and heterologous asynchronicity between identified alpha-, beta- and delta-cells within intact islets of Langerhans in the mouse
Abstract
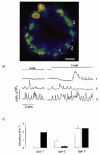
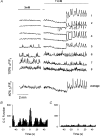
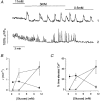
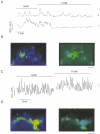
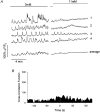
1. Using laser scanning confocal microscopy to image [Ca2+]i within intact murine islets of Langerhans, we analysed the [Ca2+]i signals generated by glucose in immunocytochemically identified alpha-, beta- and delta-cells. 2. Glucagon-containing alpha-cells exhibited [Ca2+]i oscillations in the absence of glucose, which petered out when islets were exposed to high glucose concentrations. 3. Somatostatin-containing delta-cells were silent in the absence of glucose but concentrations of glucose as low as 3 mM elicited oscillations. 4. In pancreatic beta-cells, a characteristic oscillatory calcium pattern was evoked when glucose levels were raised from 3 to 11 mM and this was synchronized throughout the beta-cell population. Remarkably, [Ca2+]i oscillations in non-beta-cells were completely asynchronous, both with respect to each other and to beta-cells. 5. These results demonstrate that the islet of Langerhans behaves as a functional syncytium only in terms of beta-cells, implying a pulsatile secretion of insulin. However, the lack of a co-ordinated calcium signal in alpha- and delta-cells implies that each cell acts as an independent functional unit and the concerted activity of these units results in a smoothly graded secretion of glucagon and somatostatin. Understanding the calcium signals underlying glucagon and somatostatin secretion may be of importance in the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus since both glucagon and somatostatin appear to regulate insulin release in a paracrine fashion.
Figures
References
-
- Asada N, Shibuya I, Iwanaga T, Niwa K, Kanno T. Identification of α- and β-cells in intact isolated islets of Langerhans by their characteristic cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration dynamics and immunocytochemical staining. Diabetes. 1998;47:751–757. - PubMed
-
- Barbosa RM, Silva AM, Tome AR, Stamford JA, Santos RM, Rosario LM. Real time electrochemical detection of 5-HT/insulin secretion from single pancreatic islets: effect of glucose and K+ depolarisation. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1996;228:100–104. - PubMed
-
- Berts A, Ball A, Dryselius S, Gylfe E, Hellman B. Glucose stimulation of somatostatin-producing islet cells involves oscillatory Ca2+ signaling. Endocrinology. 1996a;137:693–697. - PubMed
-
- Berts A, Ball A, Gylfe E, Hellman B. Suppression of Ca2+ oscillations in glucagon-producing α2-cells by insulin/glucose and amino acids. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 1996b;1310:212–216. - PubMed
-
- Berts A, Gylfe E, Hellman B. Ca2+ oscillations in pancreatic islet cells secreting glucagon and somatostatin. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1995;208:644–649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

