Natural history of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection in children of mothers infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1
- PMID: 10228060
- PMCID: PMC4360073
- DOI: 10.1086/314764
Natural history of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection in children of mothers infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1
Abstract
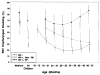
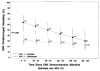
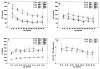
The natural history of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in 556 infants born to 517 human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1-infected mothers was studied in a prospective, multicenter, cohort study. HIV-1-infected children had a cumulative EBV infection rate similar to HIV-1-uninfected children at age 3 years (77.8% vs. 84. 9%) but had more frequent oropharyngeal EBV shedding (50.4% vs. 28. 2%; P<.001). The probability of shedding decreased with longer time from EBV seroconversion and was similar to that of HIV-1-uninfected children 3 years after seroconversion. HIV-1-infected children identified as rapid progressors shed EBV more frequently than nonrapid progressors (69.4% vs.41.0%; P=.01). HIV-1-infected children with EBV infection had higher mean CD8 cell counts. EBV infection did not have an independent effect on mean CD4 cell counts, percent CD4, IgG levels, HIV-1 RNA levels, lymphadenopathy, hepatomegaly, or splenomegaly. Early EBV infection is common in children born to HIV-1-infected mothers. Children with rapidly progressive HIV-1 disease have more frequent EBV shedding.
Figures


References
-
- Niederman JC, Evans AS. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Evans AS, Kaslow RA, editors. Viral infections of humans: Epidemiology and control. 4th ed Plenum; New York: 1997. pp. 253–83.
-
- Wang PS, Evans AS. Prevalence of antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in sera from a group of children in the People’s Republic of China. J Infect Dis. 1986;153:150–2. - PubMed
-
- Evans AS, Niederman JC, McCollum RW. Seroepidemiologic studies of infectious mononucleosis with EB virus. N Engl J Med. 1968;279:1121–7. - PubMed
-
- Niederman JC, Evans AS, Subrahmanyan L, McCollum RW. Prevalence, incidence, and persistence of EB virus antibody in young adults. N Engl J Med. 1970;282:361–5. - PubMed
-
- Greenspan JS, Greenspan D, Lennette ET, et al. Replication of Epstein-Barr virus within the epithelial cells of oral “hairy” leukoplakia, an AIDS-associated lesion. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:1564–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

