Four kinetically distinct depolarization-activated K+ currents in adult mouse ventricular myocytes
- PMID: 10228181
- PMCID: PMC2222908
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.113.5.661
Four kinetically distinct depolarization-activated K+ currents in adult mouse ventricular myocytes
Abstract
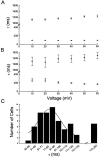
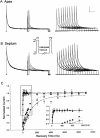
In the experiments here, the time- and voltage-dependent properties of the Ca2+-independent, depolarization-activated K+ currents in adult mouse ventricular myocytes were characterized in detail. In the majority (65 of 72, approximately 90%) of cells dispersed from the ventricles, analysis of the decay phases of the outward currents revealed three distinct K+ current components: a rapidly inactivating, transient outward K+ current, Ito,f (mean +/- SEM taudecay = 85 +/- 2 ms); a slowly (mean +/- SEM taudecay = 1,162 +/- 29 ms) inactivating K+ current, IK,slow; and a non inactivating, steady state current, Iss. In a small subset (7 of 72, approximately 10%) of cells, Ito,f was absent and a slowly inactivating (mean +/- SEM taudecay = 196 +/- 7 ms) transient outward current, referred to as Ito,s, was identified; the densities and properties of IK,slow and Iss in Ito,s-expressing cells are indistinguishable from the corresponding currents in cells with Ito,f. Microdissection techniques were used to remove tissue pieces from the left ventricular apex and from the ventricular septum to allow the hypothesis that there are regional differences in Ito,f and Ito,s expression to be tested directly. Electrophysiological recordings revealed that all cells isolated from the apex express Ito,f (n = 35); Ito,s is not detected in these cells (n = 35). In the septum, by contrast, all of the cells express Ito,s (n = 28) and in the majority (22 of 28, 80%) of cells, Ito,f is also present. The density of Ito,f (mean +/- SEM at +40 mV = 6.8 +/- 0.5 pA/pF, n = 22) in septum cells, however, is significantly (P < 0.001) lower than Ito,f density in cells from the apex (mean +/- SEM at +40 mV = 34.6 +/- 2.6 pA/pF, n = 35). In addition to differences in inactivation kinetics, Ito,f, Ito,s, and IK,slow display distinct rates of recovery (from inactivation), as well as differential sensitivities to 4-aminopyridine (4-AP), tetraethylammonium (TEA), and Heteropoda toxin-3. IK,slow, for example, is blocked selectively by low (10-50 microM) concentrations of 4-AP and by (>/=25 mM) TEA. Although both Ito,f and Ito,s are blocked by high (>100 microM) 4-AP concentrations and are relatively insensitive to TEA, Ito,f is selectively blocked by nanomolar concentrations of Heteropoda toxin-3, and Ito,s (as well as IK,slow and Iss) is unaffected. Iss is partially blocked by high concentrations of 4-AP or TEA. The functional implications of the distinct properties and expression patterns of Ito,f and Ito,s, as well as the likely molecular correlates of these (and the IK,slow and Iss) currents, are discussed.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Molecular basis of transient outward K+ current diversity in mouse ventricular myocytes.J Physiol. 1999 Dec 15;521 Pt 3(Pt 3):587-99. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1999.00587.x. J Physiol. 1999. PMID: 10601491 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of two distinct depolarization-activated K+ currents in isolated adult rat ventricular myocytes.J Gen Physiol. 1991 May;97(5):973-1011. doi: 10.1085/jgp.97.5.973. J Gen Physiol. 1991. PMID: 1865177 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular diversity of the repolarizing voltage-gated K+ currents in mouse atrial cells.J Physiol. 2000 Dec 1;529 Pt 2(Pt 2):345-58. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00345.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 11101645 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of functional voltage-gated K+ channel diversity in the mammalian myocardium.J Physiol. 2000 Jun 1;525 Pt 2(Pt 2):285-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00285.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10835033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of voltage-gated K+ channel expression in the developing mammalian myocardium.J Neurobiol. 1998 Oct;37(1):37-59. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1097-4695(199810)37:1<37::aid-neu4>3.0.co;2-9. J Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9777731 Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term administration of rosuvastatin prevents contractile and electrical remodelling of diabetic rat heart.J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2013 Aug;45(4):343-52. doi: 10.1007/s10863-013-9514-z. Epub 2013 May 3. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 2013. PMID: 23640692
-
Stabilization of Kv4 protein by the accessory K(+) channel interacting protein 2 (KChIP2) subunit is required for the generation of native myocardial fast transient outward K(+) currents.J Physiol. 2013 Sep 1;591(17):4149-66. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2013.255836. Epub 2013 May 27. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23713033 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted disruption of the Kcnq1 gene produces a mouse model of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Feb 27;98(5):2526-31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.041398998. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11226272 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating KChIP effects on Kv4.3 inactivation and recovery kinetics with a minimal KChIP2 isoform.J Physiol. 2002 Nov 15;545(1):5-11. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.031856. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 12433945 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia regulates cardiac K+ channels via O-GlcNAc-CaMKII and NOX2-ROS-PKC pathways.Basic Res Cardiol. 2020 Nov 25;115(6):71. doi: 10.1007/s00395-020-00834-8. Basic Res Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 33237428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antzelevitch, C., S. Sicouri, A. Lukas, V.V. Nesterenko, D.-W. Liu, and J.M. DiDiego. 1995. Regional differences in the electrophysiology of ventricular cells: physiological implications. In Cardiac Electrophysiology: From Cell to Bedside. D.P. Zipes and J. Jalife, editors. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia. 228–245.
-
- Anumonwo JMB, Freeman LC, Kwok WM, Kass RS. Potassium channels in the heart: electrophysiology and pharmacological regulation. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 1991;9:299–316.
-
- Barry DM, Nerbonne JM. Myocardial potassium channels: electrophysiological and molecular diversity. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:363–394. - PubMed
-
- Barry DM, Trimmer JS, Merlie JP, Nerbonne JM. Differential expression of voltage-gated K+ channel subunits in adult rat heart: relationship to functional K+channels. Circ Res. 1995;77:361–369. - PubMed
-
- Barry DM, Xu H, Schuessler RB, Nerbonne JM. Functional knockout of the cardiac transient outward current, long QT syndrome and cardiac remodelling in mice expressing a dominant negative Kv4 α subunit. Circ Res. 1998;83:560–567. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

