Different domains of the M-band protein myomesin are involved in myosin binding and M-band targeting
- PMID: 10233145
- PMCID: PMC25262
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1297
Different domains of the M-band protein myomesin are involved in myosin binding and M-band targeting
Abstract
Myomesin is a 185-kDa protein located in the M-band of striated muscle where it interacts with myosin and titin, possibly connecting thick filaments with the third filament system. By using expression of epitope-tagged myomesin fragments in cultured cardiomyocytes and biochemical binding assays, we could demonstrate that the M-band targeting activity and the myosin-binding site are located in different domains of the molecule. An N-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain is sufficient for targeting to the M-band, but solid-phase overlay assays between individual N-terminal domains and the thick filament protein myosin revealed that the unique head domain contains the myosin-binding site. When expressed in cardiomyocytes, the head domains of rat and chicken myomesin showed species-specific differences in their incorporation pattern. The head domain of rat myomesin localized to a central area within the A-band, whereas the head domain of chicken myomesin was diffusely distributed in the cytoplasm. We therefore conclude that the head domain of myomesin binds to myosin but that this affinity is not sufficient for the restriction of the domain to the M-band in vivo. Instead, the neighboring immunoglobulin-like domain is essential for the precise incorporation of myomesin into the M-band, possibly because of interaction with a yet unknown protein of the sarcomere.
Figures

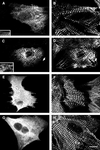
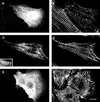
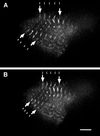
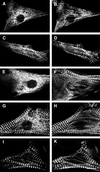
References
-
- Bähler M, Eppenberger HM, Wallimann T. Novel thick filament protein of chicken pectoralis muscle: the 86 kd protein. II. Distribution and localization. J Mol Biol. 1985;186:393–401. - PubMed
-
- Bantle S, Keller S, Haussmann I, Auerbach D, Perriard E, Mühlebach S, Perriard J-C. Tissue-specific isoforms of chicken myomesin are generated by alternative splicing. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:19042–19052. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson E, Thornell LE. Diversification of the myofibrillar M band in rat skeletal muscle during postnatal development. Cell Tissue Res. 1987;248:169–180. - PubMed
-
- Chalfie M, Tu Y, Euskirchen G, Ward WW, Prasher DC. Green fluorescent protein as a marker for gene expression. Science. 1994;263:802–805. - PubMed
-
- Craig R, Offer G. The location of C-protein in rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976;192:325–332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

