Fibronectin regulates assembly of actin filaments and focal contacts in cultured cells via the heparin-binding site in repeat III13
- PMID: 10233160
- PMCID: PMC25325
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.10.5.1521
Fibronectin regulates assembly of actin filaments and focal contacts in cultured cells via the heparin-binding site in repeat III13
Abstract
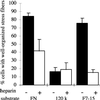
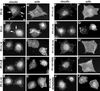
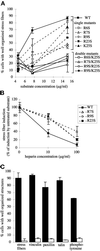
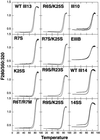
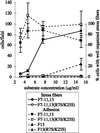
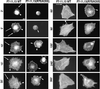
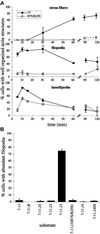
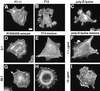
Fibroblasts, when plated on the extracellular matrix protein fibronectin (FN), rapidly spread and form an organized actin cytoskeleton. This process is known to involve both the central alpha5beta1 integrin-binding and the C-terminal heparin-binding regions of FN. We found that within the heparin-binding region, the information necessary for inducing organization of stress fibers and focal contacts was located in a 29-amino acid segment of FN type III module 13 (III13). We did not find a cytoskeleton-organizing role for repeat III14, which had previously been implicated in this process. Within III13, the same five basic amino acids known to be most important for heparin binding were also necessary for actin organization. A substrate of III13 alone was only weakly adhesive but strongly induced formation of filopodia and lamellipodia. Stress fiber formation required a combination of III13 and III7-11 (which contains the integrin alpha5beta1 recognition site), either as a single fusion protein or as separate polypeptides, and the relative amounts of the two binding sites appeared to determine whether stress fibers or filopodia and lamellipodia were the predominant actin structures formed. We propose that a balance of signals from III13 and from integrins regulates the type of actin structures assembled by the cell.
Figures




References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: Wiley; 1991.
-
- Barkalow FJ, Schwarzbauer JE. Localization of the major heparin-binding site in fibronectin. J Biol Chem. 1991;266:7812–7818. - PubMed
-
- Busby TF, Argraves WS, Brew SA, Pechik I, Gilliland GL, Ingham KC. Heparin binding by fibronectin module III-13 involves six discontinuous basic residues brought together to form a cationic cradle. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:18558–18562. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

