Human eotaxin induces eosinophil extravasation through rat mesenteric venules: role of alpha4 integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- PMID: 10233693
- PMCID: PMC2326743
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00673.x
Human eotaxin induces eosinophil extravasation through rat mesenteric venules: role of alpha4 integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
Abstract
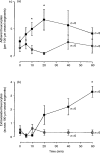
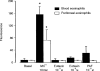
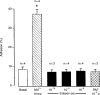
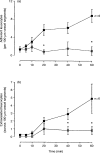
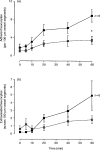
Eotaxin is a potent eosinophil-specific CC-chemokine, which has been shown to play a role in the selective induction of eosinophil accumulation in a number of allergic models of inflammation. Many aspects of the mechanism by which eotaxin induces eosinophil accumulation in vivo remain unresolved. In the present study, we investigated the direct effect of synthetic human eotaxin on leucocyte/endothelial cell interactions within rat mesenteric venules, as quantified by intravital microscopy. Topical eotaxin (30 pmol) induced rapid firm adhesion and extravasation of leucocytes within the rat mesentery, the extravasated leucocytes all being eosinophils, as determined by histological analysis. Whilst eotaxin was unable to stimulate the interaction of rat eosinophils with vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) under static conditions in vitro, eotaxin-induced responses in vivo were significantly suppressed by anti-alpha4 integrin and anti-VCAM-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). The anti-alpha4 integrin mAb, HP2/1 (3.5 mg/kg), inhibited the eotaxin-induced firm adhesion and extravasation, 60 min postapplication of the chemokine, by 89% and 84%, respectively. In the same set of experiments, the anti-VCAM-1 mAb, 5F10 (3.5 mg/kg), inhibited leucocyte adhesion and extravasation by 61% and 63%, respectively. These results demonstrate that eotaxin-induced migration of eosinophils through rat mesenteric venules in vivo is dependent on an alpha4 integrin/VCAM-1 adhesion pathway, the significance of which may only be evident under flow conditions and/or following the ligation of other adhesion molecules expressed on eosinophils.
Figures

References
-
- Griffiths-Johnson DA, Collins PD, Rossi AG, Jose PJ, Williams TJ. The chemokine, eotaxin, activates guinea-pig eosinophils in vitro, and causes their accumulation into the lung in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993;197:1167. - PubMed
-
- Palframan RT, Collins PD, Williams TJ, Rankin SM. Eotaxin induces a rapid release of eosinophils and their progenitors from the bone marrow. Blood. 1998;91:2240. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

