The lifespan of major histocompatibility complex class I/peptide complexes determines the efficiency of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses
- PMID: 10233722
- PMCID: PMC2326763
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00707.x
The lifespan of major histocompatibility complex class I/peptide complexes determines the efficiency of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses
Abstract
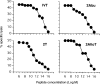
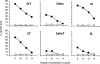
Major histocompatibility complex (MHC)/peptide association and stability are determined by specific amino acid interactions between peptide antigens and the MHC groove, and are regarded as a critical feature in ensuring efficient monitoring by T cells. In this investigation we examined the relationship between MHC/peptide stability and the immunostimulatory capacity of MHC/peptide complexes. For this purpose we compared synthetic peptide analogues derived from the immunodominant HLA-A11-presented IVTDFSVIK (IVT) epitope, for their capacity to reactivate IVT-specific memory cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) responses. The analogues differentiated from the wild-type epitope by single amino acid substitution at position 2. All peptides showed similar affinity for HLA-A11 molecules and were recognized by IVT-specific CTL clones, but induced HLA-A11 complexes at the cell surface with different lifespan. This model offered the possibility of comparing the capacity of an immunogenic epitope to stimulate a unique population of T-cell precursors depending on the lifespan of its presentation at the cell surface. We demonstrated that stable HLA-A11/peptide complexes efficiently stimulate IVT-specific CTL responses, while HLA-A11/peptide complexes with short lifespan do not. The precise identification of the role of amino acid residues in the formation of stable MHC/peptide complexes may be relevant for the design of wild-type-derived epitopes with high immunogenicity. These analogues may have important applications in the immunotherapy of infectious diseases and immunogenic tumours.
Figures
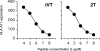
Similar articles
-
The life span of major histocompatibility complex-peptide complexes influences the efficiency of presentation and immunogenicity of two class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes in the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 4.J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):915-26. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.915. J Exp Med. 1996. PMID: 8642295 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of epitope-specific memory cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses by synthetic peptides.Clin Exp Immunol. 1996 Aug;105(2):369-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1996.d01-744.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8706347 Free PMC article.
-
An HLA-A11-specific motif in nonamer peptides derived from viral and cellular proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2217-21. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2217. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8384718 Free PMC article.
-
Hierarchies of antigen-specific cytotoxic T-cell responses.Immunol Rev. 1998 Aug;164:29-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1998.tb01205.x. Immunol Rev. 1998. PMID: 9795761 Review.
-
Identification of potential CTL epitopes of bovine RSV using allele-specific peptide motifs from bovine MHC class I molecules.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996 Nov;54(1-4):211-9. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2427(96)05686-3. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1996. PMID: 8988867 Review.
Cited by
-
In vivo analysis of CRISPR-edited germinal center murine B cells.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 17;15:1473760. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1473760. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39483469 Free PMC article.
-
Function-related regulation of the stability of MHC proteins.Biophys J. 2000 Nov;79(5):2305-13. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76476-9. Biophys J. 2000. PMID: 11053110 Free PMC article.
-
A phase 1 study of a vaccine targeting preferentially expressed antigen in melanoma and prostate-specific membrane antigen in patients with advanced solid tumors.J Immunother. 2011 Sep;34(7):556-67. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3182280db1. J Immunother. 2011. PMID: 21760528 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Unveiling the Immunogenicity of Ovarian Tumors as the Crucial Catalyst for Therapeutic Success.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 2;15(23):5694. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235694. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1 (ERAP1) trims MHC class I-presented peptides in vivo and plays an important role in immunodominance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Jun 13;103(24):9202-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0603095103. Epub 2006 Jun 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16754858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Wiley DC. Refined structure of the human histocompatibility antigen HLA-A2 at 2.6 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991;219:277. - PubMed
-
- Falk K, Rötzschke O, Stevanovic S, Jung G, Rammensee H-G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature (Lond) 1991;351:290. - PubMed
-
- Townsend AR.M, Ölen C, Bastin J, Ljunggren HG, Foster L, Kärre K. Association of class I major histocompatibility heavy and light chains induced by viral peptides. Nature (Lond) 1989;340:443. - PubMed
-
- Ljunggren H-G, Stam NJ, Öhlén C, et al. Empty MHC class I molecules come out in the cold. Nature (Lond) 1990;346:476. - PubMed
-
- Garrett TP.J, Saper MA, Bjorkman PJ, Strominger JL, Wiley DC. Specificity pockets for the side chains of peptide antigens in HLA Aw68. Nature (Lond) 1989;342:692. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

