Enrichment of c-kit+ Lin- haemopoietic progenitor cells that commit themselves to extrathymic T cells in in vitro culture of appendix mononuclear cells
- PMID: 10233727
- PMCID: PMC2326764
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00686.x
Enrichment of c-kit+ Lin- haemopoietic progenitor cells that commit themselves to extrathymic T cells in in vitro culture of appendix mononuclear cells
Abstract
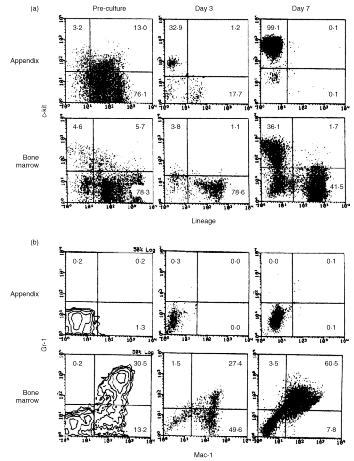
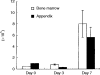
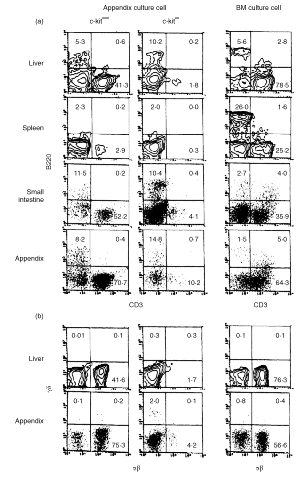
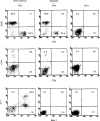
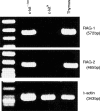
The appendix as well as the small intestine have recently been found to carry c-kit+ stem cells which give rise to extrathymic T cells. In this study, the properties of c-kit+ stem cells in the appendix of mice were further characterized. When appendix mononuclear cells (MNC) were cultured in the presence of stem cell factor, interleukin-3, interleukin-6 and erythropoietin on a methylcellulose culture plate, the population of c-kitdull Lin- and that of c-kithi Lin- cells expanded. Morphological study revealed that these c-kithi Lin- cells were basophilic granular cells (possibly mast cells). Both populations of cultured appendix MNC were then injected into severe combined immunodeficient mice or cultured with Tst-4 thymic stroma cells. These in vivo and in vitro studies demonstrated that c-kitdull Lin- cells were oligopotent haemopoietic progenitor cells which gave rise to extrathymic T cells, while c-kithi Lin- cells lacked haemopoietic progenitor cell activity. In contrast to c-kit+ stem cells in the bone marrow, those in the appendix did not give rise to myeloid cells and conventional thymic T cells under any of the conditions tested. The present results suggest that the appendix primarily comprises c-kit+ cells which give rise to basophilic granular cells and extrathymic T cells and that such c-kit+ cells have the ability to replicate themselves in culture in vitro.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intrinsic and microenvironmental defects are involved in the age-related changes of Lin - c-kit+ hematopoietic progenitor cells.Rejuvenation Res. 2007 Dec;10(4):459-72. doi: 10.1089/rej.2006.0524. Rejuvenation Res. 2007. PMID: 17663641
-
Development of intraepithelial T lymphocytes in the intestine of irradiated SCID mice by adult liver hematopoietic stem cells from normal mice.J Hepatol. 1999 Apr;30(4):681-8. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(99)80200-1. J Hepatol. 1999. PMID: 10207811
-
Hematopoietic stem cells found in lineage-positive subsets in the bone marrow of 5-fluorouracil-treated mice.Stem Cells. 1995 Sep;13(5):517-23. doi: 10.1002/stem.5530130509. Stem Cells. 1995. PMID: 8528101
-
T-cell development: an extrathymic perspective.Immunol Rev. 2006 Feb;209:103-14. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00341.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16448537 Review.
-
Isolation of human hematopoietic stem cells.Blood Cells. 1994;20(1):15-23; discussion 24. Blood Cells. 1994. PMID: 7527677 Review.
Cited by
-
Extramedullary hematopoiesis mimicking acute appendicitis: a rare complication of idiopathic myelofibrosis.Virchows Arch. 2006 Aug;449(2):258-61. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0230-5. Virchows Arch. 2006. PMID: 16738896
References
-
- Taniguchi H, Toyoshima T, Fukao K, Nakauchi H. Presence of hematopoietic stem cells in the adult liver. Nature Med. 1996;2:198. - PubMed
-
- Narita J, Miyaji C, Watanabe H, et al. Differentiation of forbidden T cell clones and granulocytes in the parenchymal space of the liver in mice treated with estrogen. Cell Immunol. 1998;185:1. - PubMed
-
- Saito H, Kanamori Y, Takemori T, et al. Generation of intestinal T cells from progenitors residing in gut cryptopatches. Science. 1998;280:275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

