Characterization of a surface membrane molecule expressed by natural killer cells in most inbred mouse strains: monoclonal antibody C9.1 identifies an allelic form of the 2B4 antigen
- PMID: 10233732
- PMCID: PMC2326752
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00709.x
Characterization of a surface membrane molecule expressed by natural killer cells in most inbred mouse strains: monoclonal antibody C9.1 identifies an allelic form of the 2B4 antigen
Erratum in
- Immunology. 2003 Oct;110(2):287
Abstract
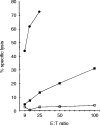
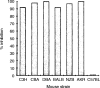
A newly generated monoclonal antibody (mAb C9.1) described in this study identifies a surface membrane molecule that is involved in the lytic programme of activated natural killer (NK) cells. This conclusion is based on the facts that, first, this antigen was expressed on the vast majority of surface immunoglobulin (sIg)- CD3- CD4- CD8- spleen lymphocytes, albeit it was also present on minor subsets of sIg+ B (approximately 7%) and CD3+ T (approximately 2%) lymphocytes; second, that all splenic NK activity was contained within the C9.1+ cell population, and was almost totally abolished by treatment of spleen cells with mAb C9.1 and complement; third, that mAb C9.1 was capable of increasing interleukin-2-cultured and in vivo polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid-activated, NK cell-mediated, antibody-redirected lysis, but not freshly isolated NK cell-mediated killing. Furthermore, the strain distribution of the C9.1 antigen was shown to be antithetical to that of the 2B4 antigen already described as a molecule associated with major histocompatibility complex-unrestricted killing mediated by activated NK cells. The gene encoding C9.1 antigen was linked to the Akp1 isozyme locus on chromosome 1 close to the 2B4 gene. Although C9.1 and 2B4 were monomeric glycoproteins of 78 000 MW and 66 000 MW, respectively, removal of N-linked sugars from both antigens by endoglycosidase F yielded identical protein backbones of 38 000 MW. Thus, all of these results suggest that mAb C9.1 recognizes an allelic form of the 2B4 antigen. However, the detection of mAb C9.1-reactive antigen on a minor subset of B cells may suggest a possible reactivity of mAb C9. 1 with some product of other members of the 2B4 family genes.
Figures

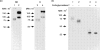
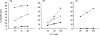
Similar articles
-
Identification of four subsets of human CD3-CD16+ natural killer (NK) cells by the expression of clonally distributed functional surface molecules: correlation between subset assignment of NK clones and ability to mediate specific alloantigen recognition.J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1589-98. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1589. J Exp Med. 1990. PMID: 2147946 Free PMC article.
-
A novel function-associated molecule related to non-MHC-restricted cytotoxicity mediated by activated natural killer cells and T cells.J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):60-70. J Immunol. 1993. PMID: 8326140
-
A new monoclonal antibody reactive with several Ly49 NK cell receptors mediates redirected lysis of target cells.Hybridoma. 1999 Aug;18(4):359-66. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1999.18.359. Hybridoma. 1999. PMID: 10571266
-
Receptors and lytic mediators regulating anti-tumor activity by the leukemic killer T cell line TALL-104.J Leukoc Biol. 2005 Aug;78(2):359-71. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0604360. Epub 2005 Jun 3. J Leukoc Biol. 2005. PMID: 15937142
-
Surface molecules involved in CD3-negative NK cell function. A novel molecule which regulates the activation of a subset of human NK cells.Int J Cancer Suppl. 1989;4:48-52. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440713. Int J Cancer Suppl. 1989. PMID: 2478490 Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotypic changes in growth-arrested T cell hybrids: a possible avenue to produce functional T cell hybridoma.Front Immunol. 2014 May 19;5:229. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00229. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24904579 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
High expression of CD244 and SAP regulated CD8 T cell responses of patients with HTLV-I associated neurologic disease.PLoS Pathog. 2009 Dec;5(12):e1000682. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000682. Epub 2009 Dec 4. PLoS Pathog. 2009. PMID: 19997502 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement of homotypic NK-cell interactions through 2B4(CD244)/CD48 in the generation of NK effector functions.Blood. 2006 Apr 15;107(8):3181-8. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-01-0185. Epub 2005 May 19. Blood. 2006. PMID: 15905190 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biron CA. Activation and function of natural killer cell responses during viral infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 1997;9:24. - PubMed
-
- Bancroft GJ. The role of natural killer cells in innate resistance to infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993;5:503. - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama WM, Seaman WE. The Ly-49 and NKR-P1 gene families encoding lectin-like receptors on natural killer cells. The NK gene complex. Annu Rev Immunol. 1993;11:613. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

