An in vivo comparison of bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and cytokine-secreting BCG vaccines
- PMID: 10233736
- PMCID: PMC2326794
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00702.x
An in vivo comparison of bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) and cytokine-secreting BCG vaccines
Abstract
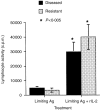
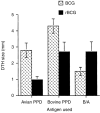
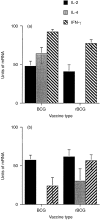
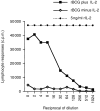
A recombinant bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine has been developed, which constitutively secretes interleukin (IL)-2. Groups of deer were immunized with either normal BCG (Pasteur 1173 P2 strain) or recombinant BCG (rBCG/IL-2) and their immune responses were monitored over 3 months. Animals gained weight over this period and showed no signs of adverse reactions to either vaccine. Lymphocyte transformation responses did not differ significantly between the two groups. No antibody that was specific for BCG was detected in any animal. Intradermal skin-test responses to BCG antigens showed that the rBCG/IL-2 induced a smaller delayed-type hypersensitivity response than the normal BCG. Cytokine transcription was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). While IL-2 and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) levels did not differ significantly between the two groups, the level of IL-4 was found to be lower in the group given rBCG/IL-2. This resulted in a strong interferon-gamma:IL-4 ratio, suggesting a skewing of the immune response towards a Type 1 response. The rate at which the vaccine was eliminated from the host was the same regardless of whether BCG or rBCG was used. At autopsy (3 months after vaccination) 99.99% of the organisms had been eliminated. The small number of organisms isolated from the draining lymph node of animals given rBCG/IL-2 were grown in antibiotic-containing media. They were shown to still contain the shuttle plasmid and to secrete biologically active IL-2, indicating that the plasmid was stably maintained despite the host's immune response and in the absence of antibiotic selection.
Figures

References
-
- Griffin JFT, Buchan GS. Aetiology, pathogenesis and diagnosis of Mycobacterium bovis infection in deer. Vet Microbiol. 1994;40:193. - PubMed
-
- Comstock GW. Field trials of tuberculosis vaccines: how could we have done them better? Contr Clin Trials. 1994;15:247. - PubMed
-
- Fine PE. Variation in protection by BCG: implications of and for heterologous immunity. Lancet. 1995;346:1339. - PubMed
-
- Griffin JFT, MacKintosh CG, Buchan GS. Animal models of protective immunity in tuberculosis to evaluate candidate vaccines. Trends Microbiol. 1995;3:418. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher PA. A strategy to improve the efficacy of vaccination against tuberculosis and leprosy. Immunol Today. 1992;13:342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

