Immunophenotypical and functional heterogeneity of dendritic cells generated from murine bone marrow cultured with different cytokine combinations: implications for anti-tumoral cell therapy
- PMID: 10233743
- PMCID: PMC2326781
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00728.x
Immunophenotypical and functional heterogeneity of dendritic cells generated from murine bone marrow cultured with different cytokine combinations: implications for anti-tumoral cell therapy
Abstract
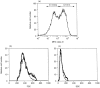
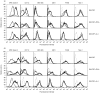
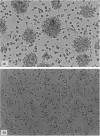
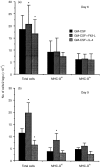
Dendritic cells (DC) are professional antigen-presenting cells that can be used as immune adjuvant for anti-tumoural therapies. This approach requires the generation of large quantities of DC that are fully characterized on the immunophenotypical and functional levels. In a murine model, we analysed the in vitro effects of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) alone or combined with interleukin-4 (IL-4) or Flt3 ligand (Flt3-L) on the number, immunophenotype and functions of bone marrow-derived DC. In GM-CSF cultures, we have identified two populations based on their level of expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules: MHC-IIhi cells, exhibiting the typical morphology and immunophenotype of myeloid DC (CD11c+ 33D1+ DEC-205+ F4/80+), and MHC-IIlo cells, heterogeneous for DC markers (30% CD11c+; 50% 33D1+; DEC-205-; F4/80+). The addition of Flt3-L to GM-CSF induced a twofold increase in MHC-IIhi DC number; besides, the MHC-IIlo cells lost all DC markers. In contrast, after addition of IL-4 to GM-CSF, the two populations displayed a very similar phenotype (CD11c+ 33D1- DEC-205+ F4/80-), differing only in their expression levels of MHC class II and costimulatory molecules, and showed similar stimulatory activity in mixed leucocyte reaction. We next analysed the migration of these cultured cells after fluorescent labelling. Twenty-four hours after injection into the footpads of mice, fluorescent cells were detected in the draining popliteal lymph nodes, with an enhanced migration when cells were cultured with GM-CSF+Flt3-L. Finally, we showed that MHC-IIhi were more efficient than MHC-IIlo cells in an anti-tumoral vaccination protocol. Altogether, our data highlight the importance of characterizing in vitro-generated DC before use in immunotherapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of interleukin-4 on the phenotype and function of bone marrow-derived murine dendritic cells generated under serum-free conditions.Scand J Immunol. 2005 Mar;61(3):251-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2005.01556.x. Scand J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15787742
-
Anti-melanoma vaccinal capacity of CD11c-positive and -negative cell populations present in GM-CSF cultures derived from murine bone marrow precursors.Vaccine. 2013 Jan 2;31(2):354-61. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.10.114. Epub 2012 Nov 10. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23146677
-
Polyethylene glycol-modified GM-CSF expands CD11b(high)CD11c(high) but notCD11b(low)CD11c(high) murine dendritic cells in vivo: a comparative analysis with Flt3 ligand.J Immunol. 2000 Jul 1;165(1):49-58. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.1.49. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10861034
-
Cytokines in the generation and maturation of dendritic cells: recent advances.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2002 Apr-Jun;13(2):186-99. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2002. PMID: 12101074 Review.
-
Induction of dendritic cells (DC) by Flt3 Ligand (FL) promotes the generation of tumor-specific immune responses in vivo.Crit Rev Immunol. 1998;18(1-2):99-107. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v18.i1-2.110. Crit Rev Immunol. 1998. PMID: 9419452 Review.
Cited by
-
Design of a highly selective quenched activity-based probe and its application in dual color imaging studies of cathepsin S activity localization.J Am Chem Soc. 2015 Apr 15;137(14):4771-7. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00315. Epub 2015 Apr 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2015. PMID: 25785540 Free PMC article.
-
Dendritic cells the tumor microenvironment and the challenges for an effective antitumor vaccination.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:425476. doi: 10.1155/2012/425476. Epub 2012 Mar 15. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22505809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells prevent disruption of the gut barrier, preserve microbiota composition, and potentiate immunoregulatory pathways in a rat model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.Gut Microbes. 2022 Jan-Dec;14(1):2127455. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2127455. Gut Microbes. 2022. PMID: 36184742 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular but not humoral immune responses generated by vaccination with dendritic cells protect mice against leukaemia.Immunology. 2000 Jan;99(1):8-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.2000.00933.x. Immunology. 2000. PMID: 10651935 Free PMC article.
-
GM-CSF Monocyte-Derived Cells and Langerhans Cells As Part of the Dendritic Cell Family.Front Immunol. 2017 Oct 23;8:1388. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01388. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 29109731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Steinman RM. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271. - PubMed
-
- Guéry J-C, Adorini L. Dendritic cells are the most efficient in presenting endogenous naturally processed self-epitopes to class II-restricted T cells. J Immunol. 1995;154:536. - PubMed
-
- Inaba K, Steinman RM. Protein-specific helper T-lymphocyte formation initiated by dendritic cells. Science. 1985;229:475. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

