High level expression of Nramp1G169 in RAW264.7 cell transfectants: analysis of intracellular iron transport
- PMID: 10233755
- PMCID: PMC2326790
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1999.00672.x
High level expression of Nramp1G169 in RAW264.7 cell transfectants: analysis of intracellular iron transport
Abstract
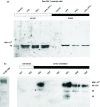
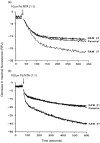
Nramp1 (natural resistance-associated macrophage protein) was positionally cloned as the defective biallelic locus in inbred mouse strains associated with uncontrolled proliferation of obligate intracellular macrophage pathogens. The causative defect was described as G169D within membrane spanning domain 4 of a transporter. The biochemical activity of Nramp1 is implied from sequence conservation with Nramp2. Nramp2 encodes a divalent cation transporter and is the carrier of a defect in models of microcytic anaemia, associated with impaired intestinal iron uptake. Iron sequestration has been proposed as an antimicrobial mechanism. Therefore, such an activity for Nramp1 is consistent with model systems. Here we showed that Nramp1 directs iron transport within the macrophage. We describe stable, high-level Nramp1G169 allele-derived polypeptide expression in Balb/c Nramp1D169 RAW264.7 cells. Transfectants express levels, comparable to those in Nramp1G169-resistant macrophages, of a 90-100x103 MW Nramp1 polypeptide. Expression of the Nramp1 polypeptide correlates with lower cellular iron loads and a reduced chelatable iron pool following challenge with iron: nitrilotriacetate. Pulse chase experiments support an enhanced iron flux in expressing cells. These data are supported using the fluorescent iron probe calcein. In Nramp1G169-expressing cells we observed an increased iron flux into the cytoplasm from a calcein-inaccessible cellular location. These data suggest Nramp1, in resting macrophage cells, mobilizes iron, from an intracellular vesicle, which is destined for cell secretion. We propose that under these conditions Nramp1 plays a role in a salvage pathway of iron recycling.
Figures
References
-
- Blackwell JM. Structure and function of the natural-resistance-associated macrophage protein (Nramp1), a candidate protein for infectious and autoimmune disease susceptibility. Mol Med Today. 1996;2:205. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell JM, Searle S. Understanding the multiple functions of Nramp1. Res Immunol. 1998 in press. - PubMed
-
- Blackwell JM, Searle S. Genetic regulation of macrophage activation: understanding the function of Nramp1 ( = Ity/Lsh/Bcg) Immunol Letts. 1999;65:73. - PubMed
-
- Vidal SM, Malo D, Vogan K, Skamene E, Gros P. Natural resistance to infection with intracellular parasites: isolation of a candidate for Bcg. Cell. 1993;73:469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

