RGD inclusion in the hexon monomer provides adenovirus type 5-based vectors with a fiber knob-independent pathway for infection
- PMID: 10233980
- PMCID: PMC112562
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.73.6.5156-5161.1999
RGD inclusion in the hexon monomer provides adenovirus type 5-based vectors with a fiber knob-independent pathway for infection
Abstract
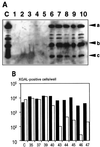
Hypervariable region 5 (HVR5) is a hydrophilic, serotypically nonconserved loop of the hexon monomer which extrudes from the adenovirus (Ad) capsid. We have replaced the HVR5 sequence of Ad5 with that of heterologous peptides and studied their effects on virus viability and peptide accessibility. A poliovirus model epitope was first inserted in a series of nine "isogenic" viruses that differed in their flanking spacers. Whereas virus productivity was not profoundly altered by any of these modifications, immunoprecipitation experiments under nondenaturing conditions demonstrated that epitope recognition by its cognate monoclonal antibody (C3 MAb) was strongly linker dependent and correlated perfectly with the ability of C3 MAb to inhibit transgene delivery and expression. An alphav-specific ligand (DCRGDCF) was then inserted in a suitable linker context to investigate whether hexon-modified capsids would enhance the transduction of cells displaying limiting amounts of the virus attachment receptors. Interestingly, although hexon has never been implicated in Ad entry, the modified virus significantly increased the transduction of human vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro. Competition experiments with 293 cells saturated with recombinant knob further indicated that the hexon-modified virus could use an additional, knob-independent pathway for entry. We concluded that genetic engineering of the Ad5 hexon monomer constitutes a novel and feasible approach to equip the virus with additional targeting ligands.
Figures



References
-
- Athapilly F K, Murali R, Rux J J, Cai Z, Burnett R M. The refined crystal structure of hexon, the major coat protein of adenovirus type 2, at 2.9 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994;242:430–455. - PubMed
-
- Bergelson J M, Cunningham J A, Droguett G, Kurt-Jones E A, Krithivas A, Hong J S, Horwitz M S, Crowell R L, Finberg R W. Isolation of a common receptor for coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science. 1997;275:1320–1323. - PubMed
-
- Blanche, F. Personal communication.
-
- Clayman G L, el-Naggar A K, Lippman S M, Henderson Y C, Frederick M, Merritt J A, Zumstein L A, Timmons T M, Liu T J, Ginsberg L, Roth J A, Hong W K, Bruso P, Goepfert H. Adenovirus-mediated p53 gene transfer in patients with advanced recurrent head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16:2221–2232. - PubMed
-
- Crompton J, Toogood C I A, Wallis N, Hay R T. Expression of a foreign epitope on the surface of the adenovirus hexon. J Gen Virol. 1994;75:133–139. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

