CD95 ligand (Fas-L/APO-1L) and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand mediate ischemia-induced apoptosis in neurons
- PMID: 10234013
- PMCID: PMC6782733
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-10-03809.1999
CD95 ligand (Fas-L/APO-1L) and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand mediate ischemia-induced apoptosis in neurons
Abstract
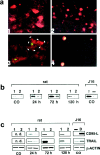
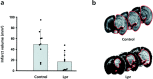
Programmed cell death plays an important role in the neuronal degeneration after cerebral ischemia, but the underlying mechanisms are not fully understood. Here we examined, in vivo and in vitro, whether ischemia-induced neuronal death involves death-inducing ligand/receptor systems such as CD95 and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL). After reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion in adult rats, both CD95 ligand and TRAIL were expressed in the apoptotic areas of the postischemic brain. Further recombinant CD95 ligand and TRAIL proteins induced apoptosis in primary neurons and neuron-like cells in vitro. The immunosuppressant FK506, which most effectively protects against ischemic neurodegeneration, prevented postischemic expression of these death-inducing ligands both in vivo and in vitro. FK506 also abolished phosphorylation, but not expression, of the c-Jun transcription factor involved in the transcriptional control of CD95 ligand. Most importantly, in lpr mice expressing dysfunctional CD95, reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion resulted in infarct volumes significantly smaller than those found in wild-type animals. These results suggest an involvement of CD95 ligand and TRAIL in the pathophysiology of postischemic neurodegeneration and offer alternative strategies for the treatment of cardiovascular brain disease.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Involvement of CD95/Apo1/Fas in cell death after myocardial ischemia.Circulation. 2000 Aug 22;102(8):915-20. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.102.8.915. Circulation. 2000. PMID: 10952962
-
FK506 prevents stroke-induced generation of ceramide and apoptosis signaling.Brain Res. 1999 May 1;826(2):210-9. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(99)01288-3. Brain Res. 1999. PMID: 10224298
-
Thyroid carcinoma cells are resistant to FAS-mediated apoptosis but sensitive to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.Cancer Res. 2000 Aug 1;60(15):4122-9. Cancer Res. 2000. PMID: 10945619
-
The CD95 (APO-1/Fas) and the TRAIL (APO-2L) apoptosis systems.Exp Cell Res. 2000 Apr 10;256(1):58-66. doi: 10.1006/excr.2000.4840. Exp Cell Res. 2000. PMID: 10739652 Review. No abstract available.
-
Tuning the rheostat of the myelopoietic system via Fas and TRAIL.Crit Rev Immunol. 2003;23(4):301-22. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v23.i4.30. Crit Rev Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14700272 Review.
Cited by
-
Apoptosis in human embryo development: 3. Fas-induced apoptosis in brain primary cultures.J Cell Mol Med. 2001 Oct-Dec;5(4):417-28. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2001.tb00177.x. J Cell Mol Med. 2001. PMID: 12067476 Free PMC article.
-
BID mediates neuronal cell death after oxygen/ glucose deprivation and focal cerebral ischemia.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Dec 18;98(26):15318-23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.261323298. Epub 2001 Dec 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001. PMID: 11742085 Free PMC article.
-
Abeta(31-35)-induced neuronal apoptosis is mediated by JNK-dependent extrinsic apoptosis pathway.Neurosci Bull. 2009 Dec;25(6):361-6. doi: 10.1007/s12264-009-0629-5. Neurosci Bull. 2009. PMID: 19927172 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropathological and biochemical features of traumatic injury in the developing brain.Neurotox Res. 2003;5(7):475-90. doi: 10.1007/BF03033158. Neurotox Res. 2003. PMID: 14715432 Review.
-
Role of Caspase-8 and Fas in Cell Death After Spinal Cord Injury.Front Mol Neurosci. 2018 Apr 3;11:101. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2018.00101. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29666570 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Angel P, Hattori K, Smeal T, Karin M. The jun protooncogene is positively autoregualted by its product Jun/AP-1. Cell. 1988;55:875–885. - PubMed
-
- Barone FC, Knudsen DJ, Nelson AH, Feuerstein GZ, Willette RN. Mouse strain differences in susceptibility to cerebral ischemia are related to cerebral vascular anatomy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1993;13:683–692. - PubMed
-
- Becher B, D’Souza SD, Troutt AB, Antel JP. Fas expression on human fetal astrocytes without susceptibility to Fas-mediated cytotoxicity. Neuroscience. 1998;84:627–634. - PubMed
-
- Brunner T, Yoo NJ, La Face D, Ware CF, Green DR. Activation-induced cell death in murine T cell hybridomas. Differential regulation of Fas (CD95) versus Fas ligand expression by cyclosporin A and FK506. Int Immunol. 1996;8:1017–1026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
