Change in the shape of dendritic spines caused by overexpression of drebrin in cultured cortical neurons
- PMID: 10234022
- PMCID: PMC6782714
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-10-03918.1999
Change in the shape of dendritic spines caused by overexpression of drebrin in cultured cortical neurons
Abstract
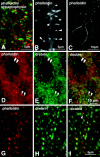
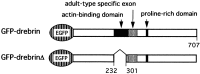
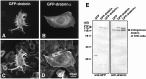
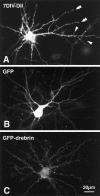
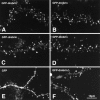
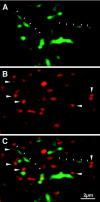
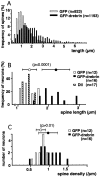
Dendritic spines are known to be extremely motile, providing a structural mechanism for synaptic plasticity. Actin filaments are thought to be responsible for the changes in the shape of spines. We tested our hypothesis that drebrin, an actin-binding protein, is a regulator of spine shape. In high-density long-term primary cultures of rat cerebral cortex neurons, drebrin was colocalized with actin filaments at spines. We introduced drebrin tagged with green fluorescent protein (GFP) into these neurons to test the ability of exogenous drebrin to localize at spines and the effect of overexpression of drebrin on spine shape. We observed that exogenous drebrin indeed accumulated in spines. But when the actin-binding domain of drebrin was deleted, the protein was distributed in both spines and dendritic shafts, indicating that accumulation of drebrin in the spines required its actin-binding activity. Statistical analysis of the lengths of spines as determined from confocal laser microscopic images revealed that the spines were significantly longer in GFP-drebrin-expressing neurons than in GFP-expressing neurons. The longer spines labeled with GFP-drebrin were demonstrated to be postsynaptic by double labeling of the presynaptic terminals with antibody against synaptophysin. These results directly indicate that drebrin binds to actin filaments at dendritic spines and alters spine shape.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drebrin-dependent actin clustering in dendritic filopodia governs synaptic targeting of postsynaptic density-95 and dendritic spine morphogenesis.J Neurosci. 2003 Jul 23;23(16):6586-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-16-06586.2003. J Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 12878700 Free PMC article.
-
Modulatory role of drebrin on the cytoskeleton within dendritic spines in the rat cerebral cortex.J Neurosci. 1996 Nov 15;16(22):7161-70. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-22-07161.1996. J Neurosci. 1996. PMID: 8929425 Free PMC article.
-
The role of drebrin in dendritic spines.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Oct;84:85-92. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Feb 1. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28161364 Review.
-
Making of a Synapse: Recurrent Roles of Drebrin A at Excitatory Synapses Throughout Life.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1006:119-139. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-56550-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 28865018 Review.
-
Overexpression of drebrin A in immature neurons induces the accumulation of F-actin and PSD-95 into dendritic filopodia, and the formation of large abnormal protrusions.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005 Dec;30(4):630-8. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 16456930
Cited by
-
Role of drebrin A in dendritic spine plasticity and synaptic function: Implications in neurological disorders.Commun Integr Biol. 2009 May;2(3):268-70. doi: 10.4161/cib.2.3.8166. Commun Integr Biol. 2009. PMID: 19641748 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase seven bundles filamentous actin and regulates dendritic spine morphology and density.EMBO Rep. 2021 Apr 7;22(4):e50145. doi: 10.15252/embr.202050145. Epub 2021 Mar 15. EMBO Rep. 2021. PMID: 33719157 Free PMC article.
-
Drebrin-like protein DBN-1 is a sarcomere component that stabilizes actin filaments during muscle contraction.Nat Commun. 2015 Jul 6;6:7523. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8523. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26146072
-
In vivo, competitive blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors induces rapid changes in filamentous actin and drebrin A distributions within dendritic spines of adult rat cortex.Neuroscience. 2006 Jul 21;140(4):1177-87. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.03.009. Epub 2006 May 2. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16650941 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of drebrin binding site on F-actin.J Mol Biol. 2010 May 14;398(4):542-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.03.039. Epub 2010 Mar 27. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20347847 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Asada H, Uyemura K, Shirao T. Actin-binding protein, drebrin, accumulates in submembranous regions in parallel with neuronal differentiation. J Neurosci Res. 1994;38:149–159. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BW, Bamburg JR. Tropomyosin binding to F-actin protects the F-actin from disassembly by brain actin-depolymerizing factor (ADF). Cell Motil. 1982;2:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Craven SE, Bredt DS. PDZ proteins organize synaptic signaling pathways. Cell. 1998;93:495–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
