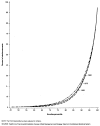
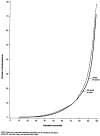
Changes in distribution of Medicare expenditures among aged enrollees, 1969-82
- PMID: 10311496
- PMCID: PMC4191524
Changes in distribution of Medicare expenditures among aged enrollees, 1969-82
Abstract
In this article, we examined the concentration of Medicare expenditures among the aged for 1969, 1975, and 1982 to determine if expenditures have become more concentrated among a few heavy users of service over time. Despite an increase in reimbursements for the aged from $6.0 billion in 1969 to $41.8 billion in 1982, the distribution of those expenses remained remarkably stable, with a slight lessening in the concentration of reimbursements in 1982. Patterns were similar for both Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (supplementary medical insurance) services. The concentration of expenditures was much greater among survivors than among people who died in both 1975 and 1982, with little change in the distribution of expenditures within either group.
Figures
References
-
- Andersen R, Lion J, Anderson O. Two Decades of Health Services: Social Survey Trends in Use and Expenditure. Cambridge, Mass.: Ballinger Publishing Co.; 1976.
-
- Birnbaum H. The Cost of Catastrophic Illness. Lexington, Mass.: Lexington Books; 1978.
-
- Board of Trustees. 1983 Annual Report of the Board of Trustees of the Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund. Washington, D.C.: Jun 24, 1983. Federal Supplementary Medical Insurance Trust Fund.
-
- Congressional Budget Office. Controlling Rising Hospital Costs. Washington, D.C.: Congress of the United States; Sept. 1979.
-
- Congressional Budget Office. Catastrophic Medical Expenses: Patterns in the Non-Elderly, Non-Poor Population. Washington, D.C.: Congress of the United States; Dec. 1982.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical