Gamma-radiation induces leaf trichome formation in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 10318689
- PMCID: PMC59243
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.120.1.113
Gamma-radiation induces leaf trichome formation in Arabidopsis
Abstract
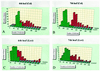
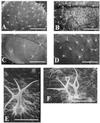
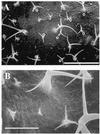
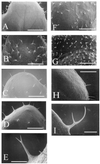
We observed induction of additional trichome formation on the adaxial surface of mature leaves of Arabidopsis after massive doses (1-3 kilograys) of gamma-radiation from cobalt-60. A typical increase in trichome number was observed in the seventh leaf when the full expansion of the fifth leaf was irradiated. Under normal growth conditions, trichome numbers on the adaxial surface of seventh leaf of the Arabidopsis ecotypes Columbia (Col) and Landsberg erecta (Ler) were 122.5 +/- 22.7 and 57.5 +/- 14.5, respectively. However, gamma-radiation induced additional trichome formation and the numbers rose to 207.9 +/- 43.7 and 95.0 +/- 27.1 in Col and Ler, respectively. In Col the shape of new trichomes was intact and their formation was spatially maintained at equal distances from other trichomes. In Ler trichome morphology was aberrant and the formation was relatively random. Treatment with antioxidants before gamma-irradiation suppressed the increase in trichome number, and treatment with methyl viologen and light induced small trichomes. These results suggest that gamma-radiation-induced trichome formation is mediated by active oxygen species generated by water radiolysis. gamma-Radiation-induced trichome formation was blocked in the trichome mutants ttg-1, gl1-1, and gl2-1. These results suggest that gamma-radiation-induced trichome formation is mediated by the normal trichome developmental pathway.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Control of GL2 expression in Arabidopsis leaves and trichomes.Development. 1998 Apr;125(7):1161-71. doi: 10.1242/dev.125.7.1161. Development. 1998. PMID: 9477315
-
Differential regulation of trichome formation on the adaxial and abaxial leaf surfaces by gibberellins and photoperiod in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh.Plant Physiol. 1996 Aug;111(4):1321-8. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.4.1321. Plant Physiol. 1996. PMID: 8756507 Free PMC article.
-
SAD2 in Arabidopsis functions in trichome initiation through mediating GL3 function and regulating GL1, TTG1 and GL2 expression.J Integr Plant Biol. 2008 Jul;50(7):906-17. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00695.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2008. PMID: 18713401
-
Progress in the molecular genetic analysis of trichome initiation and morphogenesis in Arabidopsis.Trends Plant Sci. 2000 May;5(5):214-9. doi: 10.1016/s1360-1385(00)01597-1. Trends Plant Sci. 2000. PMID: 10785667 Review.
-
A model for cell-type determination and differentiation in plants.Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1991;45:77-87. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1991. PMID: 1843415 Review.
Cited by
-
Converting low dose radiation to redox signaling.Plant Signal Behav. 2013 Feb;8(2):e23151. doi: 10.4161/psb.23151. Epub 2013 Jan 8. Plant Signal Behav. 2013. PMID: 23299433 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide transcriptome profiling of ROS scavenging and signal transduction pathways in rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to different types of ionizing radiation.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Dec;39(12):11231-48. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-2034-9. Epub 2012 Oct 20. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 23086269
-
Foliar trichome- and aquaporin-aided water uptake in a drought-resistant epiphyte Tillandsia ionantha Planchon.Planta. 2007 Dec;227(1):47-56. doi: 10.1007/s00425-007-0593-0. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Planta. 2007. PMID: 17674031
-
Effects of sparsely and densely ionizing radiation on plants.Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011 Mar;50(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00411-010-0343-8. Epub 2010 Nov 27. Radiat Environ Biophys. 2011. PMID: 21113610 Review.
-
Comparative gene expression analysis in a highly anthocyanin pigmented mutant of colorless chrysanthemum.Mol Biol Rep. 2013 Aug;40(8):5177-89. doi: 10.1007/s11033-013-2620-5. Epub 2013 May 11. Mol Biol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23666061
References
-
- Abdel-Kader AS, Moris LL, Maxie EC. Physiological studies of gamma irradiated tomato fruits. I. Effects on respiratory rate, ethylene production and ripening. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci. 1968;92:553–567.
-
- Akamine EK, Goo T. Respiration of gamma-irradiated fresh fruits. J Food Sci. 1971;36:1074–1077.
-
- Casarett AP. Radiation chemistry and effects of gamma radiation on the cell. In: Casarett AP, editor. Radiation Biology. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall; 1968.
-
- Esch JJ, Oppenheimer DG, Marks MD. Characterization of a weak allele of the GL1 gene of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol. 1994;24:203–207. - PubMed
-
- Feenstra WJ. Contiguity of linkage groups I and IV as revealed by linkage relationship of two newly isolated markers dis-1 and dis-2. Arabidopsis Inf Serv. 1978;15:35–38.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

